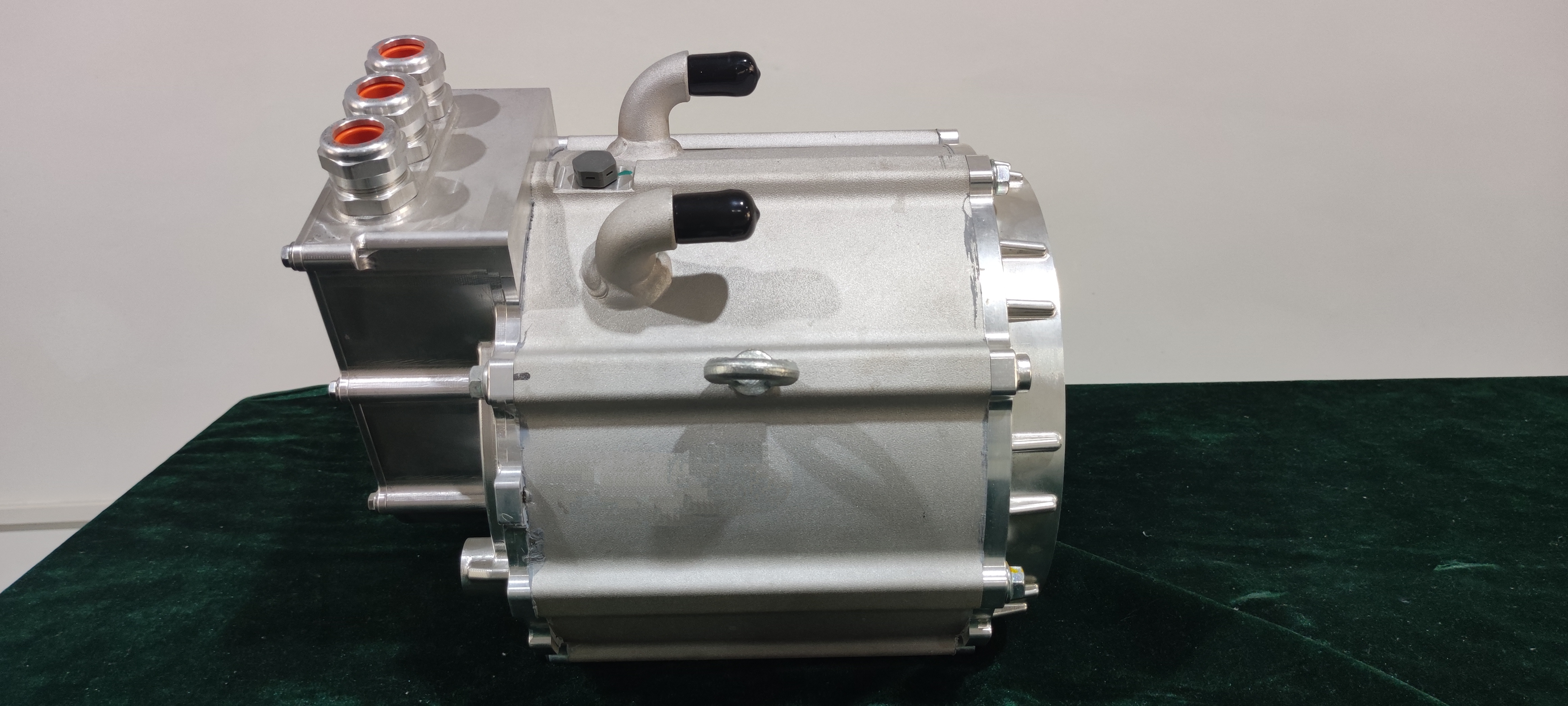
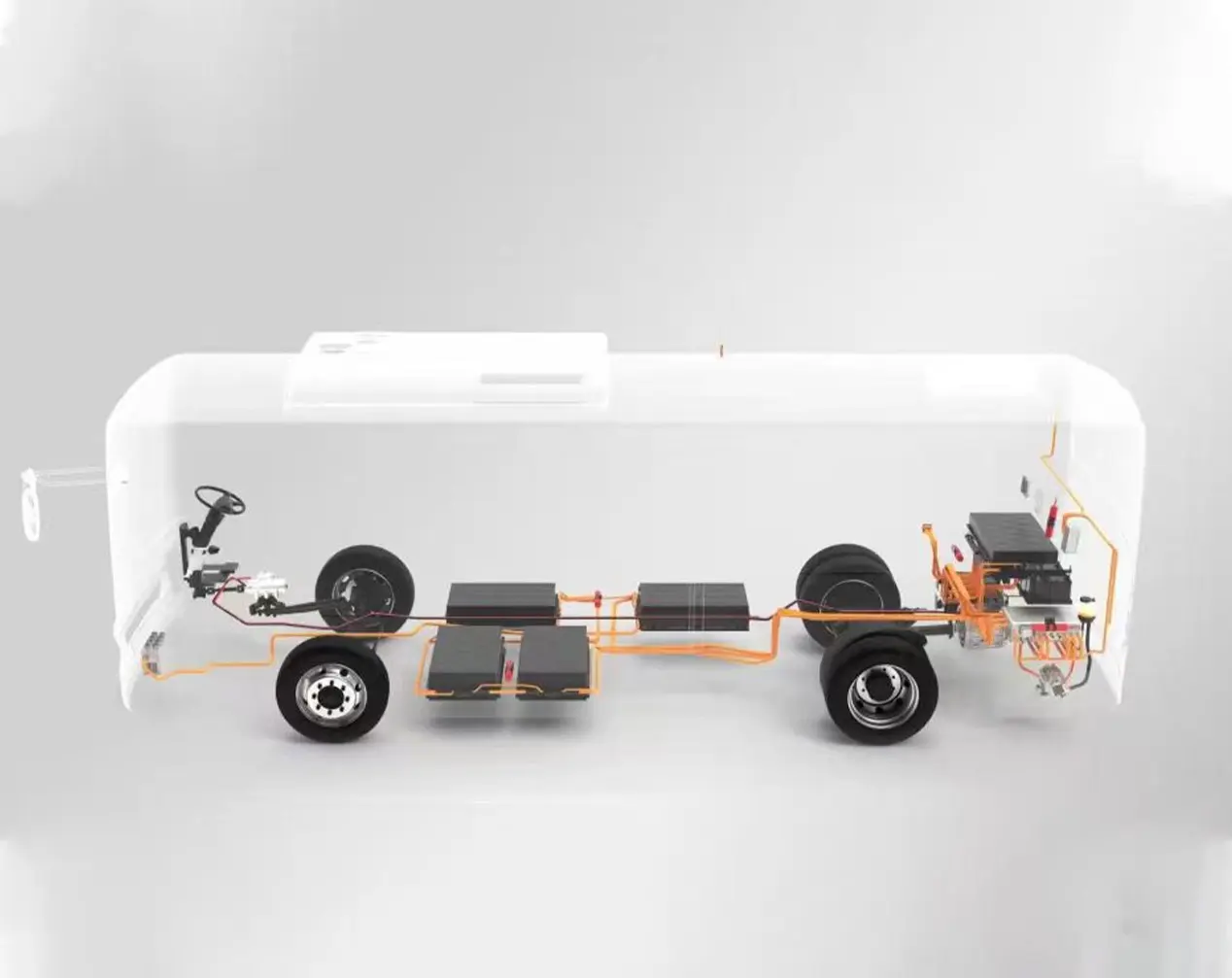
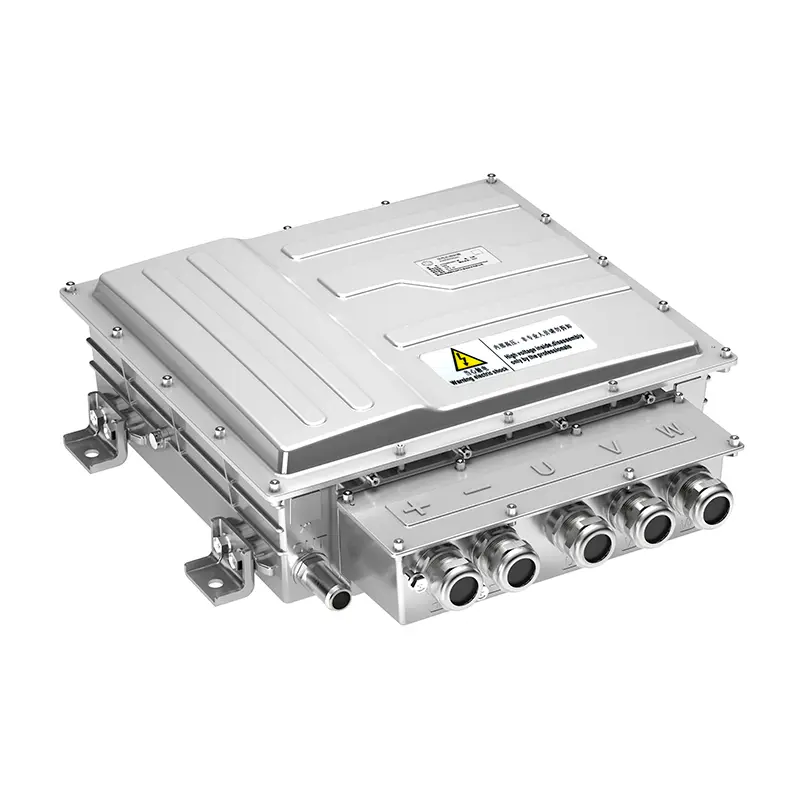
Overview on Electric Vehicle Charge Controller
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the way we think about transportation, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles. However, a critical component behind the scenes of every EV is the charging system, which ensures the battery receives the correct amount of energy efficiently and safely. At the heart of this system is the electric vehicle charge controller, a device that regulates the flow of electricity from the power source to the EV battery. This blog provides an in-depth look at EV charge controllers, covering their functions, types, features, benefits, and tips for choosing the right one.
Introduction
The rapid rise in electric vehicle (EV) adoption is transforming the automotive landscape, driven by a collective push toward reducing carbon emissions and leveraging advancements in clean energy technology. As governments, businesses, and individuals embrace this shift, the focus on ensuring efficient and reliable EV performance has become paramount. A critical aspect of this is the charging system, which serves as the lifeline for every EV, ensuring its battery is charged safely and effectively.
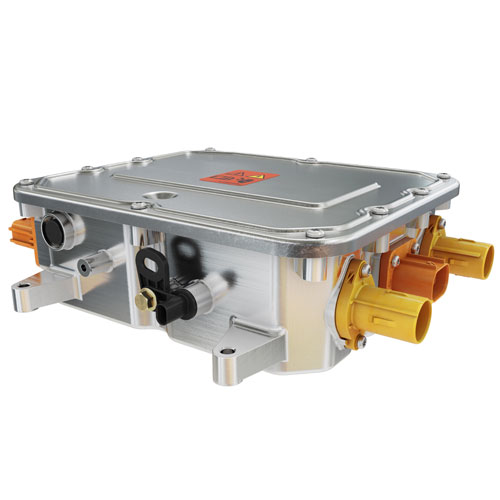
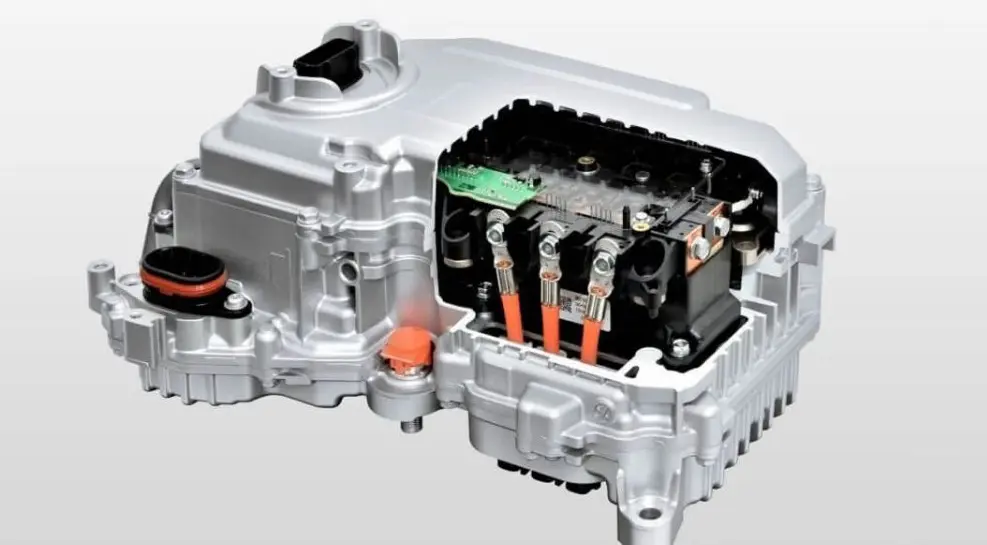
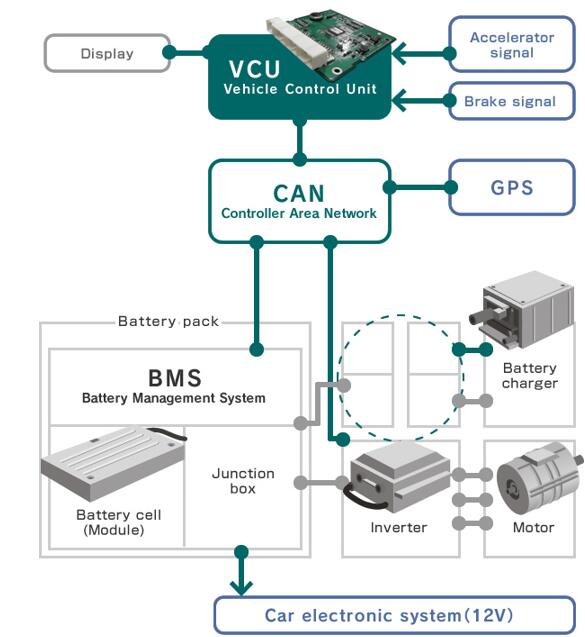
At the heart of this charging system is the electric vehicle charge controller, a sophisticated component that plays a vital role in managing and optimizing the charging process. Often referred to as the "brain" of the charging system, the charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the power source to the EV battery, ensuring it receives the correct voltage and current while preventing issues like overcharging, overheating, or short circuits. Without this crucial component, the safety, efficiency, and longevity of an EV battery would be compromised.
Whether you're an experienced EV owner or just starting your journey into electric mobility, understanding the role of the charge controller is essential. It not only impacts your vehicle's performance but also influences your overall charging experience and long-term battery health. By exploring how charge controllers work, their types, and key features, you can make informed decisions about the charging infrastructure that best suits your needs, ensuring a smoother transition to a more sustainable and eco-friendly driving future.
Key Functions of an EV Charge Controller
The electric vehicle charge controller is a cornerstone of the EV charging process, performing critical functions that ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability. By managing the flow of electricity to the battery, the charge controller optimizes charging while protecting the vehicle and its components. Below are its key functions in detail:
1. Voltage Regulation
Every EV battery operates within a specific voltage range to ensure its safety and longevity. The charge controller adjusts the voltage supplied by the power source, aligning it with the battery's requirements. Overvoltage can lead to battery damage, reduced lifespan, or even hazardous situations, making voltage regulation a vital function.
2. Current Limiting
In addition to regulating voltage, the charge controller manages the current flow to the battery. Excessive current can cause overheating, damage to battery cells, or failure of electrical components. By keeping the current within safe limits, the charge controller ensures the battery is charged efficiently without compromising safety.
3. Battery Monitoring
Modern charge controllers are equipped with sensors to track critical battery parameters, including voltage, temperature, and state of charge (SOC). This continuous monitoring enables the controller to adjust the charging process dynamically, ensuring optimal and safe charging while preventing overcharging or undercharging.
4. Load Management
In environments where multiple EVs are charging, such as at public stations or fleet depots, the charge controller helps distribute power evenly. This prevents overloading the grid, minimizes energy wastage, and ensures fair access to charging for all connected vehicles.
5. Safety Features
To safeguard the vehicle, battery, and charging infrastructure, charge controllers incorporate safety mechanisms like surge protection, short-circuit prevention, and thermal management. These features mitigate risks, enhancing the reliability of the overall charging system.
Through these essential functions, the EV charge controller plays a pivotal role in supporting the performance, safety, and sustainability of electric vehicles.
6. Charging process control
It controls the start and end of charging and the exchange of data during charging, such as the state of the battery (SOC), charging current and voltage, etc., to ensure safe and efficient charging.
7. Two-way communication
Support two-way information exchange between the vehicle and the charging pile, including charging status report, fault information, and payment information, etc., to improve the user experience.
8. Specific function support
such as supporting CCS (Combined Charging System) AC and DC combined charging function, dual gun parallel charging, etc., to provide a more flexible charging solution.
In summary, the EV charge controller is a key component to ensure safe, efficient and compatible charging, which enables the EV to seamlessly interface with the charging infrastructure and optimize the charging experience through complex communication protocols and control logic.
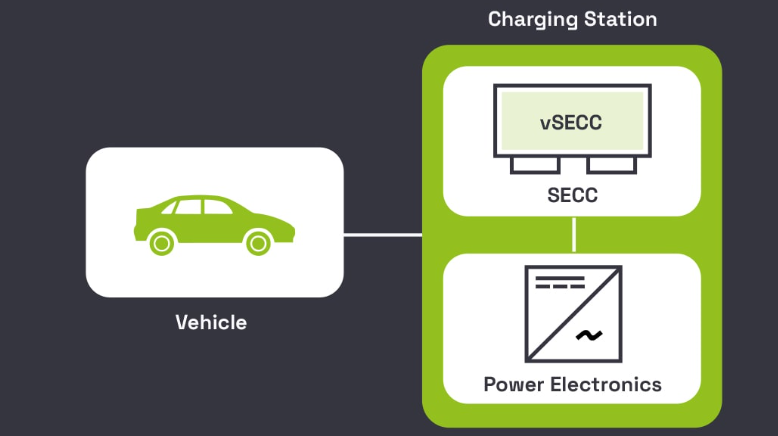
Types of Electric Vehicle Charge Controllers
There are various types of electric vehicle charge controllers, each designed for specific charging environments and requirements. Understanding these types can help you select the right one for your needs.
a. AC Charge Controllers
AC charge controllers are used in Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which deliver alternating current (AC) power to the EV. These are commonly found in residential and commercial charging setups and are suitable for slower, overnight charging.
b. DC Charge Controllers
DC charge controllers are primarily used in Level 3 fast chargers. These controllers manage direct current (DC) charging, which bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger and delivers energy directly to the battery. This allows for rapid charging, making them ideal for highway rest stops and commercial charging stations.
c. Smart Charge Controllers
Smart charge controllers come with advanced features such as connectivity to the internet or local networks. They support communication protocols like OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol), enabling remote monitoring, scheduling, and integration with smart grids or renewable energy sources.
d. On-Board Charge Controllers
These controllers are built into the vehicle itself and are responsible for regulating the charging process when using AC power from the grid. They are particularly useful for vehicles charged at home or in locations without advanced charging infrastructure.
How an EV Charge Controller Works
The electric vehicle charge controller acts as the brain of the charging system, orchestrating the safe and efficient transfer of electricity from the grid to the EV battery. Its operation involves a series of steps, each designed to ensure optimal performance and protection. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Input Power Conversion
When electricity is drawn from the grid or another power source, it often arrives in a form unsuitable for direct battery charging. The charge controller converts this power—whether alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC)—to match the EV battery’s requirements. This conversion process ensures the battery receives the appropriate voltage and current, paving the way for safe charging.
Step 2: Voltage and Current Adjustment
The controller continuously regulates the voltage and current supplied to the battery. During different stages of charging, the battery may require varying amounts of power. For instance, during the initial phase, higher current may be supplied, while a tapering current is used as the battery approaches full charge. This dynamic adjustment protects the battery from overcharging and overheating.
Step 3: Battery Monitoring
Advanced charge controllers are equipped with sensors to track critical parameters such as battery temperature, voltage, and state of charge (SOC). By monitoring these parameters in real time, the controller can adapt its operations to ensure the battery remains within safe operating limits, optimizing its health and lifespan.
Step 4: Safety Checks
The charge controller incorporates safety mechanisms to detect and address potential issues like power surges, overheating, or short circuits. If anomalies are identified, it can halt the charging process to prevent damage to the battery, vehicle, or charging station.
Step 5: Communication
Modern charge controllers communicate with both the EV and the charging station, sharing real-time data about the charging process. This synchronization enhances energy transfer efficiency, enabling features like load management and remote monitoring.
By executing these steps, the charge controller ensures a reliable and secure charging experience for EV users.
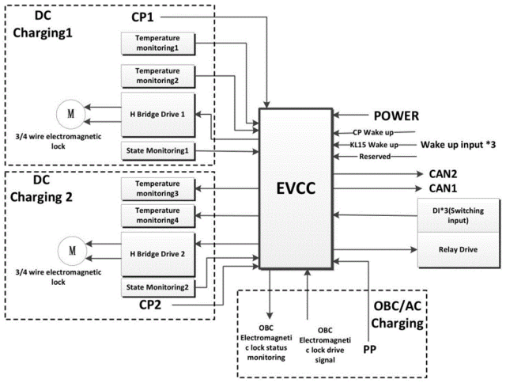
Detailed control strategy for EV charge controllers:
The control strategy of the EV charge controller is designed to enable an efficient, safe, and intelligent charging process. Its main control strategies include:
Handshake Phase:
When the electric vehicle is connected to the charging pile, the EVCC and the charging pile shake hands and establish a communication link. This phase is used to confirm the identity and status of both parties in preparation for the subsequent charging process.
Charging Parameter Negotiation:
EVCC negotiates charging parameters with EVs and charging stations, such as charging power, charging mode, etc. This step ensures that the charging process can be carried out according to the needs of the electric vehicle and the characteristics of the charging station.
Charging Phase:
During the charging process, the EVCC dynamically adjusts the output current and voltage of the charging pile according to the needs of the electric vehicle and the characteristics of the charging pile. At this stage, the charging method of constant current and then constant voltage is usually adopted to improve the charging efficiency and safety. At the initial stage of charging, a small current is used for pre-charging to heat and stabilize the characteristics of the cell. Then it enters the high-current constant current charging stage to achieve fast charging; When the battery voltage is close to the set threshold, it will switch to the constant voltage charging stage, and continue charging at a small current to prevent the battery from overcharging.
End of Charging:
After reaching the preset charging target, the EVCC sends a signal to notify the charging station to stop charging. At this time, the EVCC will also record the amount of electricity and related information during the charging process, which provides a basis for subsequent billing and management.
Software Updates & Remote Control:
EVCC supports software updates, which allow software to be updated remotely to add new features and improve performance. In addition, EVCC is intelligent and automated, with the ability to automatically identify EV models, automatically select the best charging strategy, and remotely monitor and control them via cloud services.
Features to Look for in an EV Charge Controller
When choosing an electric vehicle charge controller, it’s important to consider its features to ensure it meets your needs. Here are some key features to look for:
a. Compatibility
The charge controller must be compatible with your EV’s battery type, voltage range, and charging speed. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure a good fit.
b. Efficiency
High-efficiency controllers minimize energy loss during charging, which can save you money and reduce your carbon footprint.
c. Smart Capabilities
Controllers with smart features, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity, allow for remote monitoring and control. These features can also enable integration with home energy management systems or renewable energy sources.
d. Durability
For outdoor installations, choose a controller with robust construction and weatherproofing to withstand environmental conditions.
e. Safety Certifications
Ensure the controller meets industry safety standards, such as CE, UL, or ISO certifications, for reliable and safe operation.
f. Energy conversion and regulation
Convert the alternating current provided by the grid into direct current suitable for battery charging, including the adjustment of voltage and current to ensure the stability and efficiency of power supply.
g. Communication capability
Through a special communication unit, it can realize the information exchange with electric vehicles, charging piles and power grids, grasp the specific needs of vehicles in real time, and accurately control various parameter settings.
h. Safety and security
Equipped with multiple safety protection measures, such as over-current, over-voltage and high-temperature protection, etc., to ensure immediate response and appropriate action in abnormal situations to avoid potential damage.
i: Metering & Settlement
EVCC is able to track the actual amount of electricity consumed and generate billing details based on it, simplifying the billing process and supporting more efficient energy management.
j: Software Updates & Remote Control
EVCC supports remote upgrades, allowing you to receive the latest firmware updates over the network to introduce new features or improve performance. In addition, with the help of cloud technology, EVCC can automatically identify different EV models, select the optimal charging strategy, and implement remote monitoring.
Benefits of Using an EV Charge Controller
A high-quality electric vehicle charge controller offers numerous advantages, making it a worthwhile investment for EV owners:
a. Enhanced Battery Lifespan
By regulating the voltage and current, the charge controller protects the battery from overcharging and overheating, extending its lifespan.
b. Improved Charging Efficiency
Efficient energy transfer reduces charging time and minimizes energy loss, making the process more cost-effective.
c. Safety Assurance
Built-in safety features such as surge protection and thermal management ensure the charging process is safe for both the vehicle and the user.
d. Cost Savings
Efficient charging and extended battery life translate into significant cost savings over time, as you’ll spend less on energy and battery replacements.
e. Flexibility
Smart charge controllers allow you to schedule charging sessions, take advantage of off-peak electricity rates, and integrate with renewable energy sources.
f: Safety guarantee
EVCC has a variety of built-in protection mechanisms, such as over-current protection, over-voltage protection and temperature protection, to ensure the safety of the charging process. As soon as an anomaly is detected, EVCC takes immediate action to prevent damage to the EV or charging infrastructure.
g: Charging metering and billing
EVCC can record the amount of electricity during the charging process and provide relevant billing information accordingly. This provides users and operators with convenient charging management and statistical services.
h: Control strategy
EVCC's control strategy is designed to achieve an efficient, safe, and intelligent charging process. It is able to establish a communication link with the charging station during the handshake phase, negotiate the charging parameters, and dynamically adjust the output current and voltage of the charging station according to the needs of the electric vehicle and the characteristics of the charging station during the charging phase.
i: Software Update & Remote Control
EVCC supports software update function, which can update software remotely to add new features and improve performance. In addition, EVCC is intelligent and automated, with the ability to automatically identify EV models, automatically select the best charging strategy, and remotely monitor and control them via cloud services.
j: Global applicability
EVCC is designed to be compatible with a variety of standards, and can convert China's national standard GB/T27930 CAN communication protocol into ISO/IEC15118, DIN70121 or SAE2847-2 PLC communication standards commonly used in European and American markets, as well as Japan's CHAdeMO standard.
Through these features, EVCC can not only provide a safe and efficient charging experience, but also improve the overall performance and user satisfaction of electric vehicles through intelligent management.

How to Choose the Right Charge Controller for Your EV
Choosing the right electric vehicle charge controller is crucial for ensuring efficient, safe, and convenient charging tailored to your specific needs. The following steps will guide you through the decision-making process:
1. Assess Your Charging Needs
Begin by evaluating your charging habits and requirements. If you primarily charge your EV at home, an AC charge controller may be sufficient, offering steady and reliable power for overnight charging. However, if you frequently travel long distances or require rapid charging, a DC fast charge controller is a better choice. Consider whether you’ll need compatibility with public charging stations or plan to install a home charging setup.
2. Check Compatibility
Your EV’s battery type, voltage, and maximum charging speed are key factors to consider. Ensure the charge controller is compatible with these specifications to avoid performance issues. Some controllers are designed for specific EV brands or models, while others offer universal compatibility, making them suitable for a range of vehicles.
3. Look for Smart Features
For added convenience, opt for a charge controller with advanced features such as remote monitoring, charging schedules, and integration with smart home systems. These features allow you to manage charging from your smartphone, monitor energy consumption, and even sync with renewable energy sources like solar panels for eco-friendly charging.
4. Verify Safety Features
Safety is paramount. Look for charge controllers equipped with essential safety mechanisms, including short-circuit protection, surge protection, thermal management, and fault detection. These features safeguard your vehicle, home, and charging infrastructure from potential risks.
5. Consider Your Budget
While high-end controllers come with premium features, there are budget-friendly options that still deliver reliable and safe charging. Evaluate your needs and strike a balance between functionality and cost to find a charge controller that fits your requirements without overspending.
6. Voltage and current requirements
Determine the voltage and current range that the charge controller needs to support based on the battery system and charging needs of the electric vehicle. For example, if an electric vehicle supports different charging modes (such as AC charging and DC fast charging), the charge controller needs to be able to accommodate these different charging modes.
7. Efficiency and safety
Choose a charge controller with high efficiency and advanced safety measures. For example, a controller with MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) can optimize energy conversion and increase charging efficiency under different environmental conditions.
8. Brand and reliability
Choose a charge controller from well-known brands, the products of these brands are usually subject to strict quality control and testing, which is able to provide more stable and reliable performance.
9. Maintenance and upgrades
Consider the convenience of future maintenance and upgrades for the charge controller. Choose brands that offer good customer service and technical support for future system upgrades or breakdowns.
By considering these factors, it is possible to choose the right charge controller to ensure the charging efficiency, safety, and convenience of electric vehicles.
Conclusion
The electric vehicle charge controller is a cornerstone of EV technology, ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable charging. By understanding its functions, types, and features, you can make informed decisions about your EV charging system. Whether you’re a new EV owner or an enthusiast exploring advanced technology, investing in the right charge controller is key to optimizing your charging experience and ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s battery. As the core controller of the electric vehicle charging system, it plays an important role in power conversion and control, communication interface, safety protection, charging metering and billing. Through fine control strategies and advanced communication technology, the EV charging controller can achieve an efficient, safe and intelligent charging process, providing strong support for the popularization and promotion of EVs. With the rapid development of the electric vehicle market and the continuous advancement of technology, PUMBAA from China will continue to evolve and innovate to bring a more convenient and safe charging experience to electric vehicle users.
Read More: What is an Inverter in Electric Vehicle? What Does It Do in EV Car?