What Is a Hybrid Car?
Hybrid cars have gained significant popularity due to their fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and innovative technology that blends gasoline and electric power. Unlike conventional gasoline-powered vehicles, hybrid cars combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor to optimize performance and energy usage. This combination allows them to consume less fuel and emit fewer pollutants while still providing the range and reliability of traditional cars.
In this blog, we will explore the key aspects of hybrid vehicles, including how they differ from gasoline-powered cars, the structure of a gasoline-electric hybrid system, performance insights, fuel efficiency enhancement strategies, power split mechanisms, horsepower considerations, and tips for maximizing hybrid fuel efficiency.
Gasoline vs. Electric: A Power Source Comparison
The primary distinction between hybrid and conventional vehicles lies in their power sources. Gasoline cars rely solely on an internal combustion engine, burning fuel to generate power. In contrast, hybrid vehicles incorporate an electric motor and a battery pack alongside the ICE, enabling various modes of operation:
- Gasoline Mode – The car operates using only the internal combustion engine, similar to a conventional vehicle.
- Electric Mode – The car runs purely on electric power, using energy stored in the battery. This is common at low speeds or during light acceleration.
- Hybrid Mode – The car intelligently switches between the gasoline engine and electric motor, optimizing fuel efficiency and performance.
Hybrid cars can be categorized based on their powertrain configuration, with two major types being the parallel hybrid powertrain and the series hybrid powertrain.
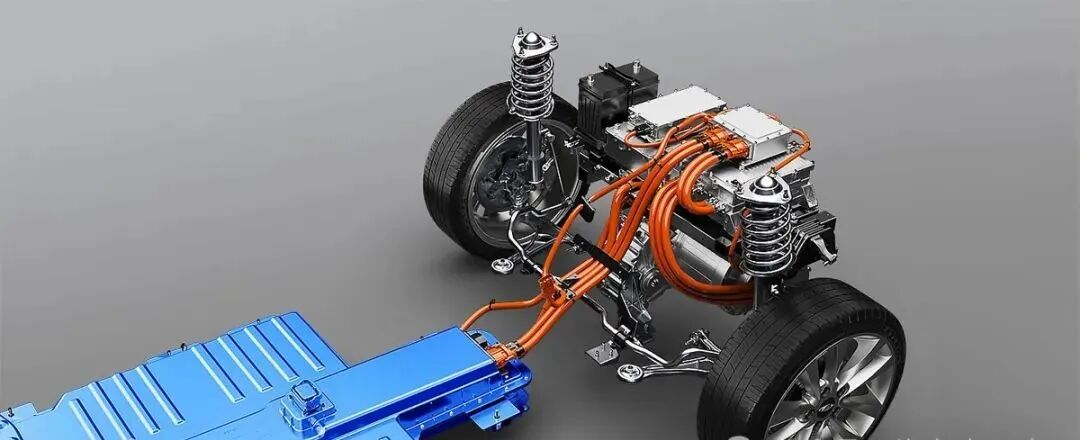
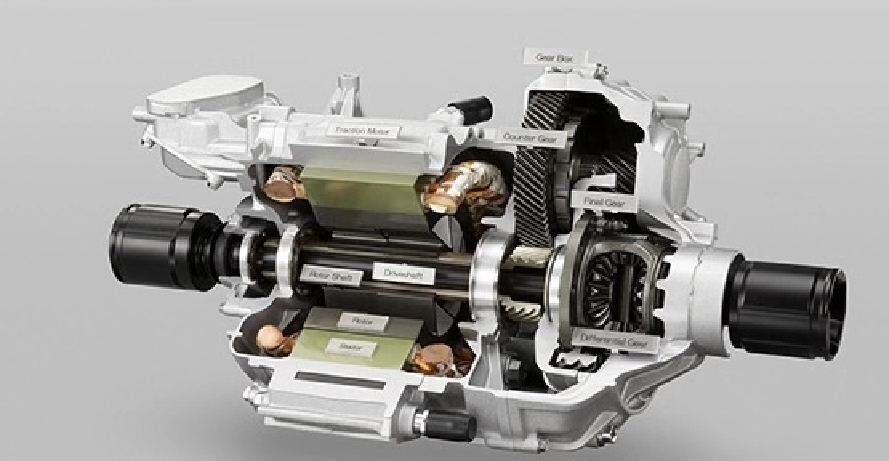
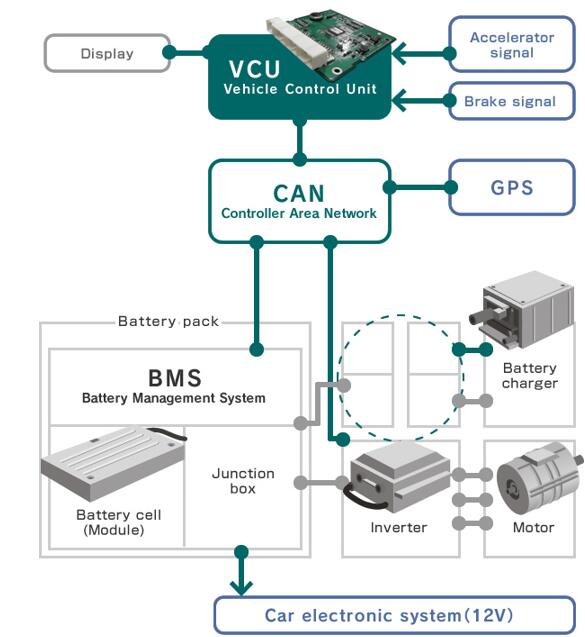
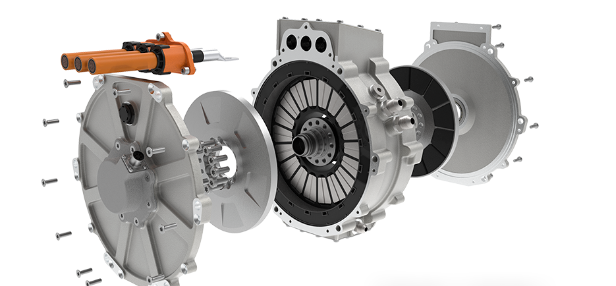
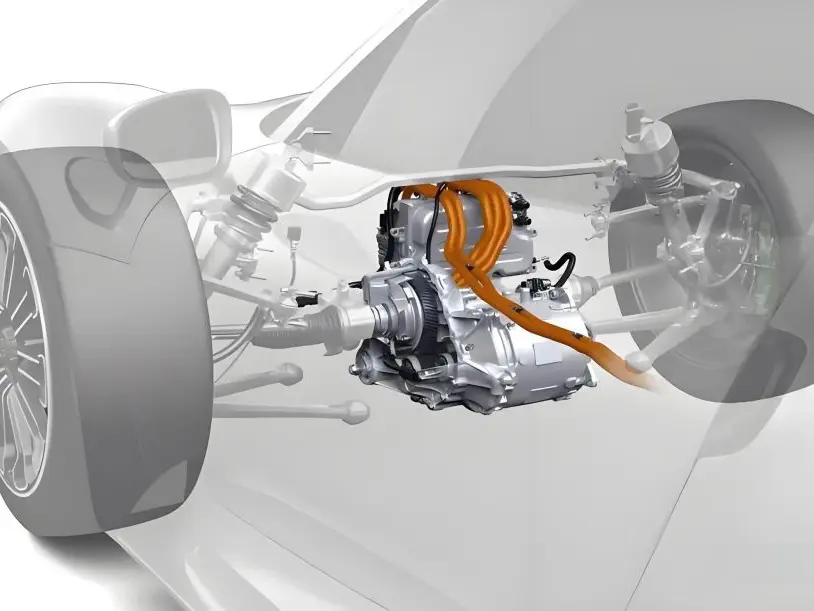
Structure of a Gasoline-Electric Hybrid System
A hybrid vehicle's gasoline-electric system consists of several key components that work together to enhance efficiency:
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) – The gasoline-powered engine provides propulsion and recharges the battery in certain configurations.
- Electric Motor – The motor powers the vehicle in electric mode and assists the engine when extra power is needed.
- Battery Pack – Stores electrical energy used to power the motor and recover energy from regenerative braking.
- Power Electronics – Manages the flow of electricity between the battery, motor, and other components.
- Regenerative Braking System – Captures kinetic energy lost during braking and converts it into electricity to recharge the battery.
Depending on the hybrid system design, the interaction between these components varies, influencing how the vehicle optimizes fuel economy and performance.
Types of Hybrid Powertrains
Parallel hybrid powertrain
A parallel hybrid powertrain integrates both an internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor to drive the vehicle. These two power sources can function simultaneously or individually, depending on driving conditions. The electric motor can assist the ICE during acceleration, hill climbing, or overtaking, enhancing efficiency and performance. Since both the engine and motor are directly connected to the drivetrain, they operate in parallel, which is where the name comes from.
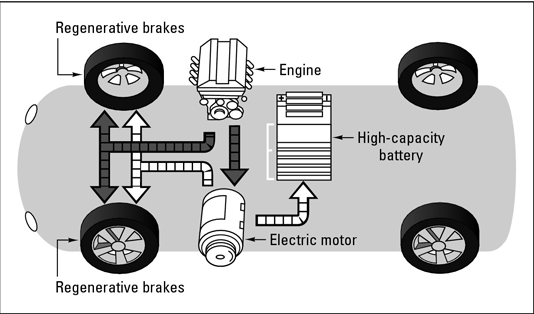
Series hybrid powertrain
A series hybrid powertrain utilizes an internal combustion engine—either gasoline or diesel—to generate electricity rather than directly powering the wheels. This engine supplies energy to a generator, which then either transfers power to the electric motor or charges a high-capacity battery for later use. In this system, the electric motor is the sole component responsible for propelling the vehicle by turning the drive axles or driveshaft, creating a smoother and quieter driving experience.
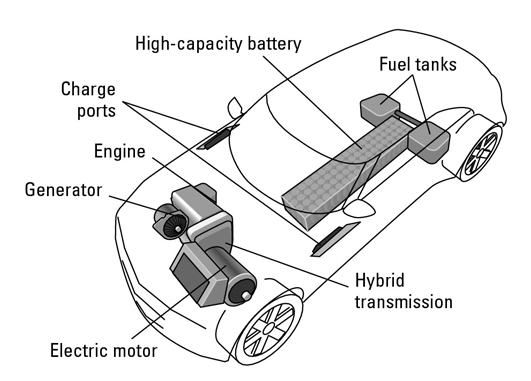
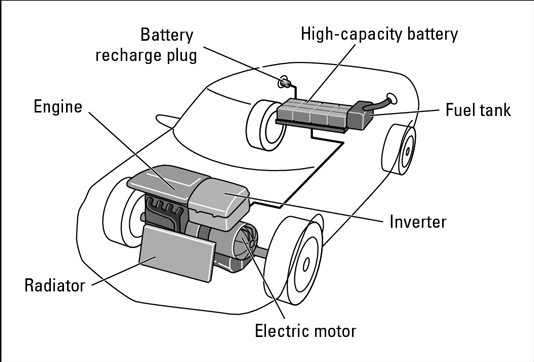
Plug-in hybrids
Plug-in hybrids come equipped with larger battery packs that can be recharged using standard household electrical outlets or dedicated charging stations. This extended battery capacity enables them to operate on electric power for significantly longer distances before relying on the internal combustion engine. Some estimates suggest that plug-in hybrids can achieve fuel efficiencies of up to 100 miles per gallon (mpg).
Certain automotive enthusiasts have modified their hybrid vehicles into plug-in models, while manufacturers are increasingly producing them in collaboration with utility companies. The key to their widespread adoption lies in the development of compact, high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that can undergo multiple recharge cycles. Future advancements could see plug-in hybrids traveling up to 125 miles solely on electric power before switching to conventional hybrid operation.
Environmental Considerations of Plug-In Hybrids
One challenge with plug-in hybrids is that their electricity supply is often sourced from power grids that rely on fossil fuels. However, efforts are being made to integrate renewable energy solutions, with some charging stations harnessing solar or wind power. Additionally, many eco-conscious hybrid owners are installing solar panels at home to recharge their vehicles sustainably.
While plug-in hybrids significantly reduce dependence on gasoline, they still require an internal combustion engine for long journeys, steep inclines, and heavy loads. Looking ahead, future hybrid models may incorporate hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, further reducing the need for gasoline-powered operation.
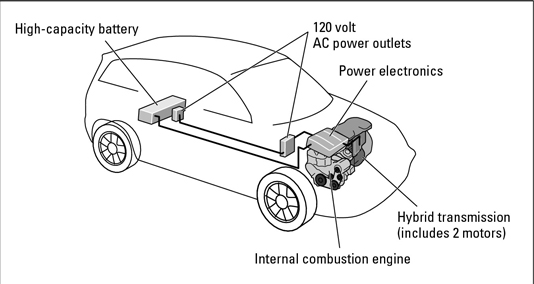
Two-mode hybrids
Two-mode hybrid technology could position the U.S. as a strong contender in the hybrid market. Unlike conventional hybrids that rely on large battery packs, two-mode hybrids feature smaller batteries along with two electric motors housed within an advanced automatic transmission. This system includes two separate gear sets—one dedicated to the internal combustion engine and another designed to enhance the electric motors' output.
At lower speeds, the vehicle can operate using one or both electric motors, either independently or in conjunction with the ICE. When higher speeds are required, the second mode engages, ensuring the ICE runs efficiently at optimal gear ratios. Additionally, the transmission in a two-mode hybrid can function similarly to a continuously variable transmission (CVT), further optimizing performance and fuel economy.
Performance Insights of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid cars are designed to provide a balance between fuel efficiency and driving performance. Here’s how they compare in key performance areas:
- Acceleration and Power – Many hybrid vehicles have parallel hybrid powertrains, where the gasoline engine and electric motor work together to deliver strong acceleration. However, hybrids are generally optimized for efficiency rather than high-speed performance.
- Fuel Economy – Hybrid cars consume significantly less fuel than conventional vehicles due to their ability to rely on electric power at low speeds and during light acceleration.
- Quiet Operation – In series hybrid powertrains, the electric motor is the primary propulsion source, resulting in a smooth and quiet driving experience.
- Regenerative Braking – Unlike traditional cars, hybrids recover energy during braking, which contributes to improved overall efficiency.
- City vs. Highway Performance – Hybrid cars tend to be more fuel-efficient in stop-and-go city driving, where the electric motor can handle much of the workload. On highways, the gasoline engine is more active, but the hybrid system still optimizes fuel usage.
Five Effective Ways to Enhance Fuel Efficiency
To get the most out of a hybrid car’s fuel efficiency, drivers can adopt the following strategies:
1.Optimize Acceleration and Braking – Smooth, gradual acceleration and braking help minimize fuel consumption by maximizing the electric motor’s contribution.
2.Utilize Regenerative Braking – Take advantage of regenerative braking to recharge the battery and reduce overall fuel consumption.
3.Monitor Tire Pressure – Keeping tires properly inflated reduces rolling resistance and improves fuel efficiency.
4.Reduce Unnecessary Weight – Carrying excess weight in the vehicle increases fuel consumption. Removing unnecessary cargo enhances efficiency.
5.Maintain Steady Speeds – Hybrid vehicles perform best at consistent speeds, so using cruise control on highways can improve fuel economy.
Understanding the Power Split Mechanism
Hybrid vehicles use a power split mechanism to determine when to use gasoline, electric power, or a combination of both. This mechanism varies depending on whether the car has a parallel hybrid powertrain or a series hybrid powertrain:
- Parallel Hybrid Powertrain – The internal combustion engine and electric motor can work independently or together. At lower speeds, the car primarily relies on the electric motor, while at higher speeds, the gasoline engine takes over. The power split is optimized to reduce fuel consumption.
- Series Hybrid Powertrain – The gasoline engine doesn’t directly drive the wheels but instead generates electricity to power the electric motor. This setup is common in plug-in hybrids and range-extender models, providing a more electric-focused driving experience.
By intelligently managing these power sources, hybrid cars achieve a seamless balance between fuel efficiency and performance.
Choosing the Right Horsepower for Your Needs
Selecting the right hybrid vehicle involves considering horsepower based on driving needs:
- City Commuters – If most driving is within urban areas, a lower-horsepower hybrid with a strong electric motor is ideal for maximizing fuel savings.
- Highway Drivers – For frequent highway travel, a hybrid with a more powerful gasoline engine ensures smooth and efficient long-distance performance.
- Towing and Heavy Loads – Some hybrid SUVs and trucks offer higher horsepower configurations to handle towing and cargo needs.
Modern hybrid vehicles come in various power outputs, ensuring that buyers can find a model that aligns with their specific driving demands.
Tips for Maximizing Hybrid Fuel Efficiency
To further improve the efficiency of hybrid vehicles, consider the following expert tips:
- Use Eco Mode – Many hybrids come with an “Eco” driving mode that adjusts throttle response and energy usage for improved fuel economy.
- Minimize Air Conditioning and Heating Usage – Excessive use of climate control can reduce efficiency by increasing the energy demand.
- Plan Routes with Fewer Stops – Avoiding traffic congestion and excessive stopping allows for more efficient hybrid operation.
- Regular Maintenance – Ensuring the hybrid system, battery, and engine are in top condition helps maintain fuel efficiency over time.
- Leverage Electric-Only Driving – In plug-in hybrid models, maximizing electric-only driving reduces fuel consumption significantly.
Conclusion
Hybrid cars represent a significant advancement in automotive technology, blending gasoline and electric power to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. With the ability to optimize power distribution through either a parallel hybrid powertrain or a series hybrid powertrain, these vehicles offer a seamless driving experience while lowering fuel costs.
Understanding the structure of a hybrid system, its performance characteristics, fuel-saving techniques, and the power split mechanism helps consumers make informed decisions about whether a hybrid car suits their lifestyle. Whether for city commuting, highway driving, or occasional towing, there is a hybrid model tailored to various needs.
By following best practices for fuel efficiency and selecting the right hybrid powertrain configuration, drivers can maximize the benefits of hybrid technology while contributing to a greener future.
Read More: Introduction to axle structure and development trend of electric drive axle