Electric Bus Motors: Which Motor is Used? Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
As cities around the world shift towards sustainable transportation, the electric bus motor is becoming a crucial element in the evolution of public transit. These motors not only power electric buses but also symbolize a move towards cleaner, more efficient travel options. In this blog, we will delve into the types of motors used, their advantages, and the future of electric bus technology.
Which Motor is Used in an Electric Bus?
The most commonly used motors in electric buses include:
Induction Motors
Often regarded as the workhorse of the electric bus motor world, induction motors offer high efficiency and reliability. They are especially popular in urban buses due to their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds, making them well-suited for city driving.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM)
These motors are known for their exceptional efficiency and compact size. The electric bus motor design that incorporates permanent magnets allows for a high power-to-weight ratio, which is beneficial in maximizing the range of the bus.
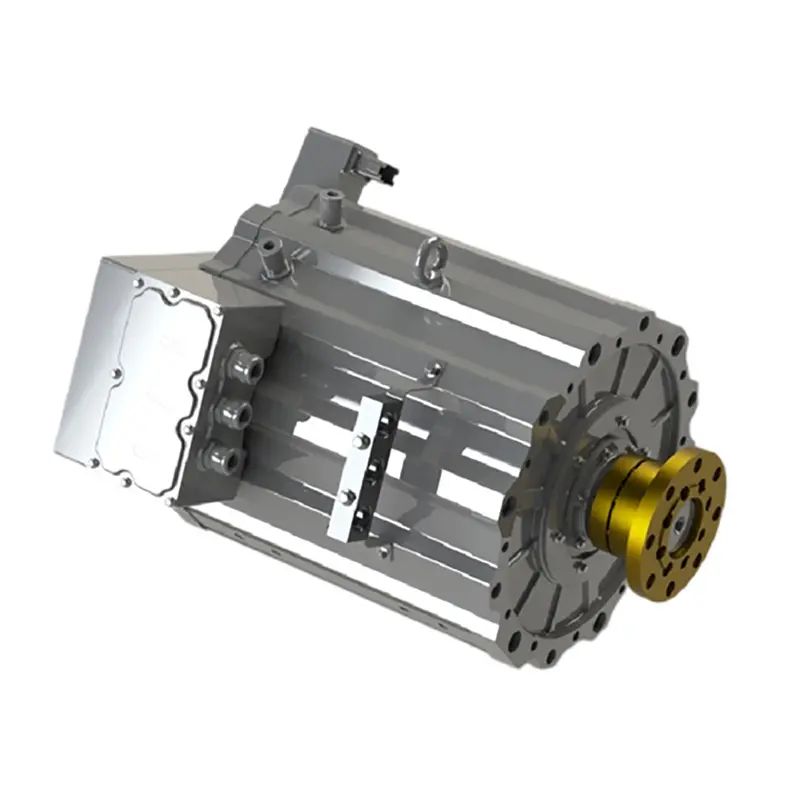
PUMBAA permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM )for Electric vehicle Drive gen5 PML080
Brushless DC Motor Drive
While less common in larger electric buses, these motors provide high efficiency and require less maintenance. They are often used in smaller electric vehicles or specific applications within the public transport sector.
Do Electric Buses Use AC or DC?
Electric buses primarily use AC (Alternating Current) motors, although some models may still incorporate DC (Direct Current) motors. The choice between AC and DC depends on various factors, including cost, efficiency, and application.
AC Motors
AC motors are preferred in most modern electric buses due to several benefits:
· Efficiency: AC motors can convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into mechanical energy, making them more efficient over a range of speeds.
· Durability: These motors typically have fewer moving parts, which translates to lower maintenance requirements.
· Performance: AC motors can maintain consistent performance at different speeds, ideal for the stop-and-go conditions prevalent in urban environments.
DC Motors
In contrast, DC motors, while simpler in design, may not be as efficient or durable as their AC counterparts. However, they can still be found in specific applications, particularly where cost considerations are paramount.
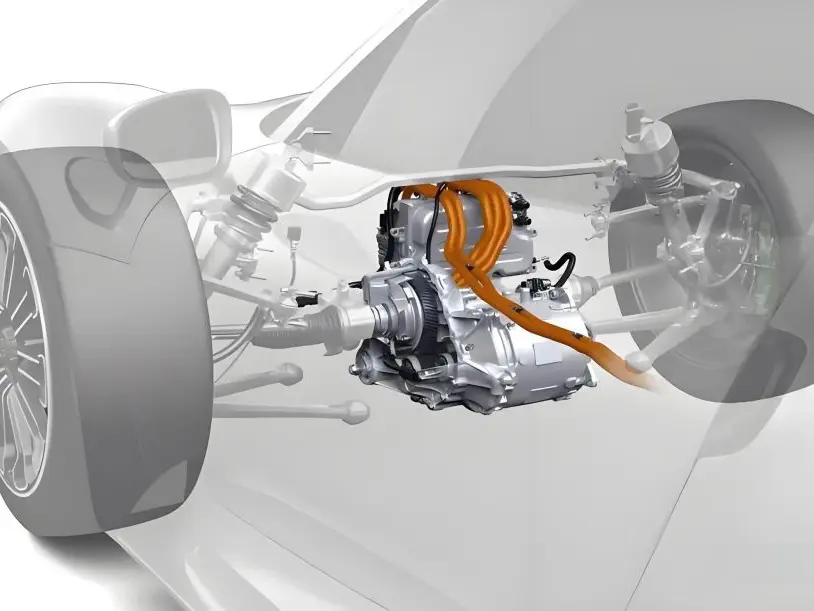
Does an Electric Bus Have an Engine?
An electric bus does not have an engine in the traditional sense, as it does not rely on an internal combustion engine (ICE) like a diesel or gasoline bus. Instead, it uses an electric motor powered by batteries or, in some cases, through a connection to overhead wires (like trolleybuses).
Key Differences:
Electric Motor vs. Internal Combustion Engine:
Electric buses are equipped with electric motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. This allows for smoother acceleration and lower emissions compared to traditional engines.
Power Source:
Electric buses rely on batteries to store energy, which is then used to power the electric motor. Some systems may use supercapacitors or even hydrogen fuel cells in certain designs.
Components:
Instead of an engine, electric buses have components such as an AC motor inverter (to convert DC from the batteries to AC for the motor), a battery management system, and regenerative braking systems that help recharge the batteries.
In summary, while electric buses do not have an engine like conventional buses, they are equipped with electric motors that perform the same role in terms of propulsion.
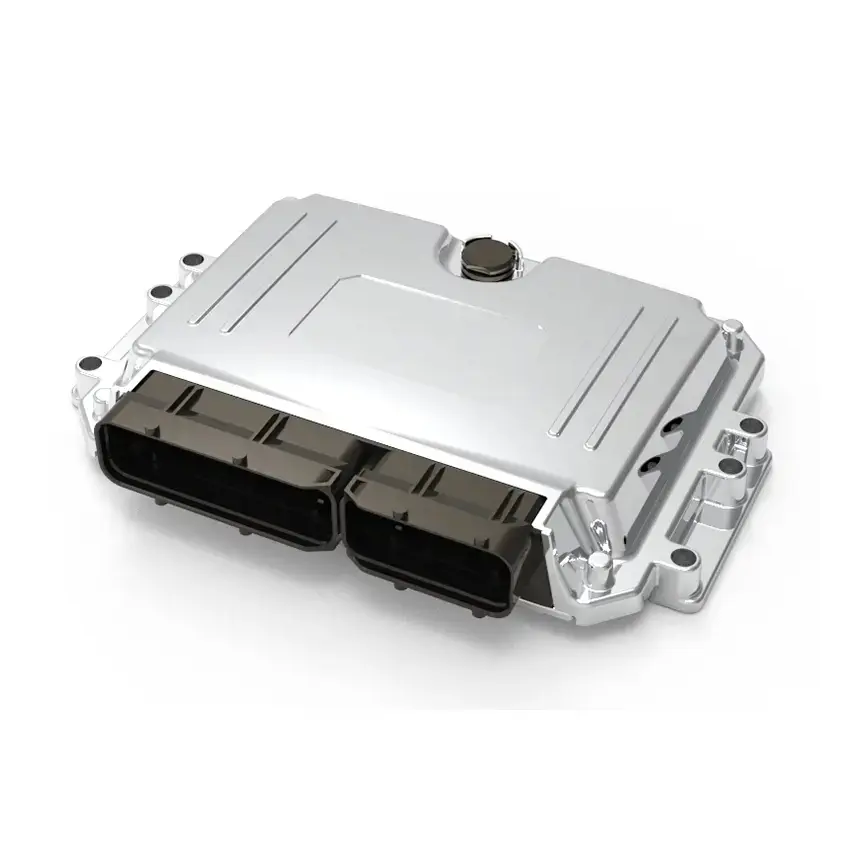
PUMBAA Electric Vehicle Drive Controller Unit PEVC007 (Applies to all models)
What are Electric Buses Powered by?
Electric buses are primarily powered by electricity stored in batteries. Here are the main power sources used:
- Batteries: Most electric buses utilize large lithium-ion batteries to store electrical energy. These batteries are charged at depots or through charging stations.
- Overhead Wires: Some electric buses, known as trolleybuses, draw power from overhead wires using a pantograph. This system allows them to operate without large onboard batteries.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A few electric buses use hydrogen fuel cells, which generate electricity by combining hydrogen with oxygen. This process emits only water vapor, making it a clean alternative.
- Supercapacitors: Some buses may incorporate supercapacitors for quick energy storage and release, especially for regenerative braking systems.
These power sources enable electric buses to operate efficiently while reducing emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
Advantages of Electric Bus Motors
The electric bus motor offers numerous advantages that contribute to the overall effectiveness and appeal of electric buses:
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant advantages is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Electric buses equipped with efficient motors produce zero tailpipe emissions, leading to improved air quality in urban areas.
Operational Cost Savings
Electric bus motors reduce fuel costs significantly compared to traditional diesel engines. Additionally, lower maintenance costs, due to fewer moving parts, further enhance the economic viability of electric buses.
Noise Reduction
Electric motors operate much quieter than internal combustion engines, significantly decreasing noise pollution in urban environments. This is especially important for cities aiming to improve residents' quality of life.
Regenerative Braking
Many electric bus motors can also incorporate regenerative braking systems, which capture energy typically lost during braking and convert it back into electrical energy, extending the bus’s range and improving efficiency.
The Future of Electric Bus Motors
As technology continues to advance, the electric bus motor is likely to evolve further. Innovations in battery technology, motor design, and power management systems are on the horizon, promising enhanced performance and efficiency.
Improved Battery Integration
Future electric bus motors will likely benefit from advancements in battery technology, enabling longer ranges and faster charging times. This will make electric buses more practical for longer routes.
Smart Motor Technologies
Integrating smart technology into electric bus motors can lead to improved efficiency through real-time monitoring and adjustments based on performance data. This could further optimize energy use and extend the lifespan of the motors.
Sustainable Materials
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, future electric bus motors may be constructed from more eco-friendly materials, reducing the environmental impact of their production.
Conclusion
The electric bus motor is at the forefront of transforming public transportation. With the combination of AC and DC technologies, these motors not only enhance the efficiency and performance of electric buses but also contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future for urban mobility. As cities embrace this technology, we can expect to see significant improvements in air quality, noise reduction, and overall public transit experiences.