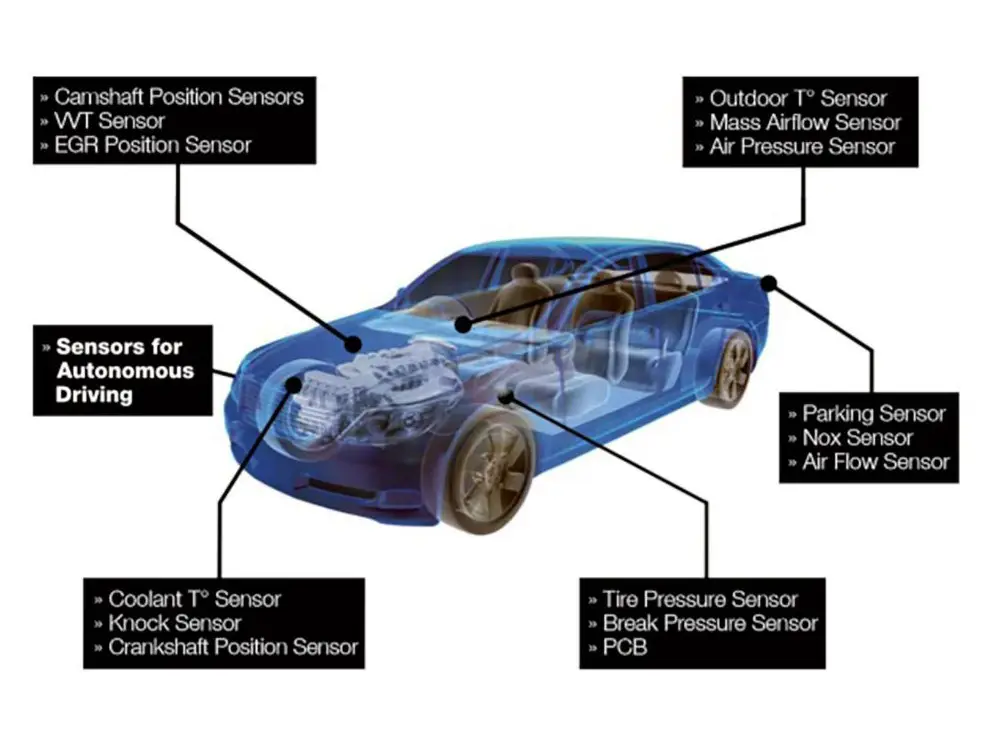
Electric Drive Motor vs. Hybrid Drive Motors: A Comprehensive Comparison
The global shift toward sustainable transportation is gaining momentum, with electric and hybrid drive motors leading the way. As more people prioritize reduced emissions and fuel efficiency, it’s essential to understand the differences between these two types of propulsion systems. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down electric and hybrid drive motors, exploring their functions, advantages, and limitations. Additionally, we will analyze the role each plays in electric gasoline hybrid cars and provide an in-depth comparison to help you choose the right technology for your needs.
Understanding Electric Drive Motors
Electric drive motors are the driving force behind fully electric vehicles (EVs), and their growing popularity represents a significant shift from traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs). These motors convert electrical energy stored in a vehicle’s battery into mechanical energy, producing motion without the need for fuel combustion. For those interested in DIY electric vehicle projects, finding a quality electric car motor for sale is essential for a smooth conversion. The primary components of an electric drive motor include:
- Rotor and Stator: These two parts create the magnetic interaction that generates torque. The rotor is the rotating part, while the stator remains stationary. Electric current passing through the stator creates a magnetic field that turns the rotor, which then drives the wheels.
- Power Electronics: This system controls the motor’s power output and speed, converting direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC) that powers the motor. Advanced power electronics also optimize efficiency and manage energy distribution based on driving conditions.
- Battery Pack: The high-capacity battery is the primary energy source for electric drive motors. It stores and supplies the electricity needed for propulsion, and its capacity largely determines the vehicle's range.
Electric drive motors are renowned for their simplicity compared to ICEs. They have fewer moving parts, which leads to less wear and tear and significantly reduces maintenance needs. Their design also allows for regenerative braking, a process where braking energy is converted back into electricity, which is then stored in the battery. This feature increases overall efficiency and range in EVs.
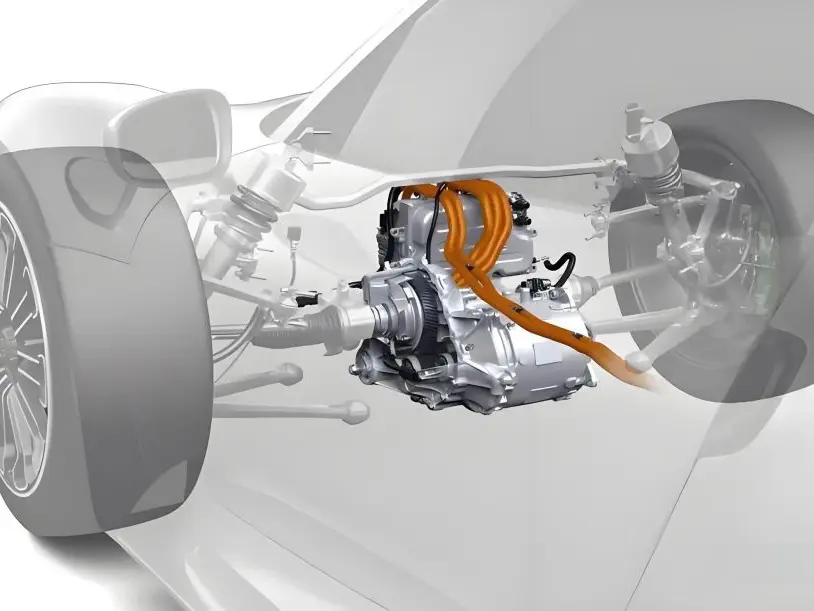
Introduction to Hybrid Drive Motors
Hybrid drive motors are used in vehicles that combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor, also known as electric gasoline hybrid cars. These vehicles, designed to maximize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, offer drivers the flexibility to use either gasoline or electric power, depending on the driving scenario. Hybrid drive motors come in several configurations, each with unique characteristics:
- Series Hybrid Systems: In a series hybrid, the electric motor is responsible for driving the wheels, while the gasoline engine generates electricity to recharge the battery. This configuration is well-suited for city driving, where low speeds and frequent stops allow the electric motor to handle most of the work.
- Parallel Hybrid Systems: In parallel hybrids, both the electric motor and gasoline engine can independently drive the wheels or work together for added power. This setup is more versatile, as it allows the vehicle to use the electric motor for low-speed driving while switching to the gasoline engine at higher speeds or during rapid acceleration.
- Series-Parallel Hybrid Systems: A combination of both series and parallel systems, series-parallel hybrids can switch seamlessly between electric and gasoline power as needed. The car’s energy management system (EMS) determines which mode to use, optimizing efficiency and performance based on speed, load, and battery charge.
Hybrid systems are ideal for reducing fuel consumption, particularly in urban environments, while still offering extended range for longer journeys where gasoline may be required. This balance makes hybrids a popular choice for drivers who want fuel efficiency without sacrificing range.
Electric Drive Motors in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric drive motors are the foundation of electric vehicles (EVs) like the Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, and Chevrolet Bolt. These cars operate exclusively on electricity stored in a battery, relying on the electric motor for all driving power. Here’s a closer look at how electric drive motors perform in EVs:
- Power Source: Electric vehicles use a large-capacity lithium-ion or, in some cases, solid-state battery. This battery supplies DC electricity to the motor, which is then converted to AC by the power electronics to drive the motor.
- Instant Torque: Electric drive motors provide instant torque, a unique characteristic of electric propulsion that delivers powerful, smooth acceleration from a standstill. This allows EVs to accelerate quickly, providing a responsive and enjoyable driving experience.
- High Efficiency: Electric motors are highly efficient, with efficiency rates often exceeding 85-90%, compared to the 20-30% efficiency of conventional gasoline engines. This means more energy is directly converted to motion, which translates to better range and lower energy waste.
- Environmental Impact: Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an environmentally friendly option. By eliminating exhaust pollutants, EVs contribute to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.
- Regenerative Braking: EVs use regenerative braking to recapture kinetic energy and store it back in the battery. This system allows the car to recover energy during braking, increasing efficiency and extending the driving range.
These features make electric drive motors a powerful and sustainable choice for reducing transportation’s environmental impact. However, range and charging infrastructure remain considerations that must be addressed for wider EV adoption.
Hybrid Drive Motors in Electric Gasoline Hybrid Cars
Electric gasoline hybrid cars, such as the Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, and Ford Fusion Hybrid, are designed to maximize fuel economy and reduce emissions by combining ICEs with electric motors. Here’s how hybrid drive motors work in these vehicles:
- Battery Assistance: Hybrid motors often operate in electric-only mode at low speeds, particularly in city driving, where stop-and-go traffic allows for short bursts of electric power. When greater speed or power is needed, the gasoline engine engages, or both power sources work in tandem for added strength.
- Energy Management: A sophisticated energy management system (EMS) controls the balance between electric and gasoline power. This system can automatically decide when to use the electric motor, the gasoline engine, or both to ensure maximum fuel efficiency. For example, the EMS might prioritize the electric motor at low speeds, switch to the gasoline engine on highways, and use both during acceleration.
- Regenerative Braking: Like EVs, hybrids use regenerative braking to recapture energy lost during braking. This energy is stored in the battery, improving fuel efficiency and extending electric range.
- Extended Range: Unlike EVs, hybrids can rely on gasoline power for long-distance driving, providing flexibility and eliminating range anxiety. Drivers can refuel at any gas station, making hybrids suitable for those who need a versatile vehicle capable of handling both city and highway travel.
By blending electric and gasoline power, hybrids offer improved fuel economy and reduced emissions compared to traditional gasoline-only vehicles. The ability to seamlessly switch between power sources makes hybrids an attractive option for drivers seeking both efficiency and convenience.

Comparing Electric and Hybrid Drive Systems: Key Factors
When comparing electric and hybrid drive systems, several critical factors should be considered, as each system has its strengths and weaknesses:
|
Factor |
Electric Drive Motor |
Hybrid Drive Motor |
|
Energy Source |
Battery only |
Battery and gasoline |
|
Emissions |
Zero tailpipe emissions |
Reduced emissions, but not zero |
|
Efficiency |
High, due to electric-only propulsion |
Moderate, varies with driving conditions |
|
Range |
Limited to battery capacity |
Extended with gasoline backup |
|
Maintenance |
Lower, due to fewer moving parts |
Moderate, requires both ICE and electric motor maintenance |
|
Refueling Infrastructure |
Limited, relies on charging stations |
Broadly available, can use gasoline stations |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Drive Motors
Advantages of Electric Drive Motors:
- Environmental Benefits: Electric drive motors produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Instant Torque and Smooth Acceleration: Electric motors deliver immediate torque, which allows for smooth and quick acceleration, enhancing the driving experience.
- Lower Operating Costs: Operating an EV is often cheaper than a gasoline vehicle due to lower fuel (electricity) costs and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Mechanical Simplicity: With fewer moving parts, electric drive motors are less prone to mechanical failure and require less frequent maintenance, reducing overall costs.
Disadvantages of Electric Drive Motors:
- Range Limitations: EVs are limited by battery capacity, which can cause “range anxiety” on longer trips. However, advances in battery technology are gradually improving range.
- Charging Infrastructure: While growing, the charging infrastructure is still limited in some areas, making EV travel challenging in regions with few charging stations.
- Charging Time: Fully recharging a battery can take hours, although fast-charging stations offer quicker recharging options. For some users, charging time may be less convenient than refueling a gasoline vehicle.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Drive Motors
Advantages of Hybrid Drive Motors:
- Extended Range: By combining electric and gasoline power, hybrids offer flexibility for both short trips and long journeys without concerns about running out of power.
- Lower Emissions than Conventional ICEs: Although not entirely emissions-free, hybrids emit less pollution than traditional gasoline vehicles, particularly in urban settings.
- Fuel Efficiency: Hybrids can significantly reduce fuel consumption in city driving, thanks to the electric motor handling low-speed travel.
- Versatile Refueling Options: Unlike EVs, hybrids can refuel at any gas station, making them suitable for remote areas with limited charging options.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Drive Motors:
- Complexity and Maintenance: Hybrids have both an electric motor and ICE, making the system more complex and potentially increasing maintenance costs.
- Moderate Environmental Impact: While better than gasoline-only vehicles, hybrids still produce emissions and consume fossil fuels.
- Higher Purchase Cost: Hybrid vehicles can be more expensive than conventional ICE vehicles due to the complexity of their dual systems.
The Future of Electric and Hybrid Drive Motors
The automotive industry is evolving rapidly, and both electric and hybrid drive systems are likely to see significant improvements in the coming years. Electric drive motors will benefit from advancements in battery technology, leading to longer ranges, shorter charging times, and more efficient energy use. Charging infrastructure is also expected to expand globally, making EVs increasingly convenient for a broader audience.
Hybrid drive motors may evolve to incorporate more advanced energy management systems and lightweight materials, further improving fuel efficiency. Some manufacturers are developing plug-in hybrids with larger batteries, enabling them to drive longer distances on electric power alone. This trend bridges the gap between full EVs and traditional hybrids, allowing for flexibility in regions with limited charging infrastructure.
Conclusion
Electric and hybrid drive motors each have unique strengths and limitations, catering to different needs and lifestyles. Electric drive motors offer high efficiency, zero emissions, and lower maintenance, making them ideal for those seeking a fully eco-friendly solution. Hybrid drive motors, on the other hand, provide the flexibility of an extended range with lower fuel consumption, making them a practical choice for drivers who frequently travel long distances or have limited access to charging infrastructure. By understanding the core differences between electric and hybrid drive systems, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your environmental values, driving habits, and budget.
FAQs on Electric and Hybrid Drive Motors
Q1. What is the primary difference between electric drive motors and hybrid drive motors? Electric drive motors rely solely on battery power, while hybrid drive motors combine a battery-powered electric motor with a gasoline engine, providing flexibility and extended range.
Q2. Are electric vehicles (EVs) better for the environment than hybrids?
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them more environmentally friendly than hybrids, which still rely on gasoline. However, the environmental impact of EVs also depends on the energy source for charging (e.g., renewable vs. fossil fuel power).
Q3. How does regenerative braking work in EVs and hybrids?
Regenerative braking captures energy typically lost as heat during braking, converting it into electricity and storing it in the battery, thereby increasing efficiency and range.
Q4. Are hybrid vehicles more fuel-efficient than conventional gasoline vehicles?
Yes, hybrid vehicles are generally more fuel-efficient than gasoline-only vehicles, especially in city driving, where the electric motor can handle low-speed tasks.
Q5. What is range anxiety, and how do hybrids address this concern?
Range anxiety is the concern of running out of battery power without access to a charging station. Hybrids address this by using a gasoline engine as backup, allowing drivers to continue driving if the battery is depleted.