How to Use Gas to Electric Car Conversion Kit?
Converting a gas-powered car to an electric vehicle (EV) is a fascinating and environmentally friendly way to breathe new life into an older car while benefiting from the efficiency and performance advantages of electric motors. Whether you're trying to reduce your carbon footprint, save on fuel costs, or simply explore the world of electric propulsion, converting your gas-powered vehicle to electric power can offer numerous advantages.
In this expanded guide, we’ll delve into every step of the process of converting a gas-powered car to electric, including how it works, the benefits, the costs involved, the types of vehicles suitable for conversion, and the best electric car conversion kits.
How Does Gas to Electric Car Conversion Work?
An electric vehicle conversion involves replacing the gasoline-powered engine in your vehicle with an electric motor and integrating a new powertrain and battery system. The process requires several technical steps, including the installation of electric drive systems, new wiring, and a power management system that controls the flow of electricity between the motor and the battery.
a) Removing the Gasoline Engine and Fuel System
The first significant step in an EV conversion is the removal of the internal combustion engine (ICE) and the entire fuel system. This involves draining the fuel tank, removing the exhaust system, and disconnecting all the components related to gasoline power.
- Engine Removal: The gasoline engine is typically heavier and more complicated than an electric motor. Removing the engine can be a labor-intensive task that often requires lifting equipment to handle the weight.
- Fuel System: The fuel tank, fuel lines, and exhaust system are all dismantled. This is necessary to make room for the new electric components, particularly the battery pack and the electric motor.
- Transmission System: In some conversions, the car's existing transmission is retained to allow the electric motor to connect to the wheels. However, many conversions opt for a simpler single-speed gear system, as electric motors don't require multi-gear transmissions to function effectively. This simplifies the conversion and enhances the efficiency of the vehicle.
b) Installing the Electric Motor
Once the gasoline engine is removed, the next step is to install the electric motor. The motor is the core of the conversion and determines the overall performance of the vehicle. The type of motor you choose depends on the weight of the car, the desired performance, and the range you expect.
- DC Motors: These are often used in older or simpler EV conversions because they are cheaper and easier to work with, but they can be less efficient and require more maintenance.
- AC Motors: More modern and efficient, AC motors are preferred for high-performance EV conversions. They offer smoother acceleration, better energy efficiency, and can be more easily controlled with advanced systems.
- Permanent Magnet Motors: This type of motor uses permanent magnets in the rotor, which increases efficiency. They are common in high-performance EVs due to their ability to deliver higher power output with fewer components.
c) Fitting the Battery Pack
The battery pack provides the power needed for the electric motor to run. Lithium-ion batteries are typically the preferred option for EV conversions due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
- Battery Size and Range: The size of the battery pack you install will directly affect the driving range of the vehicle. Larger battery packs provide more power and thus a longer range but can add significant weight to the car. A typical EV battery might range from 10 kWh to 40 kWh for most conversions, depending on the desired range and driving conditions.
- Battery Management System (BMS): A BMS is essential for ensuring the batteries operate efficiently and safely. It monitors each battery cell’s voltage and temperature to prevent overcharging or overheating, which could damage the battery.
- Mounting: Batteries must be mounted securely to avoid shifting during operation. This often involves fabricating custom mounts to hold the battery pack in place, ensuring optimal weight distribution.
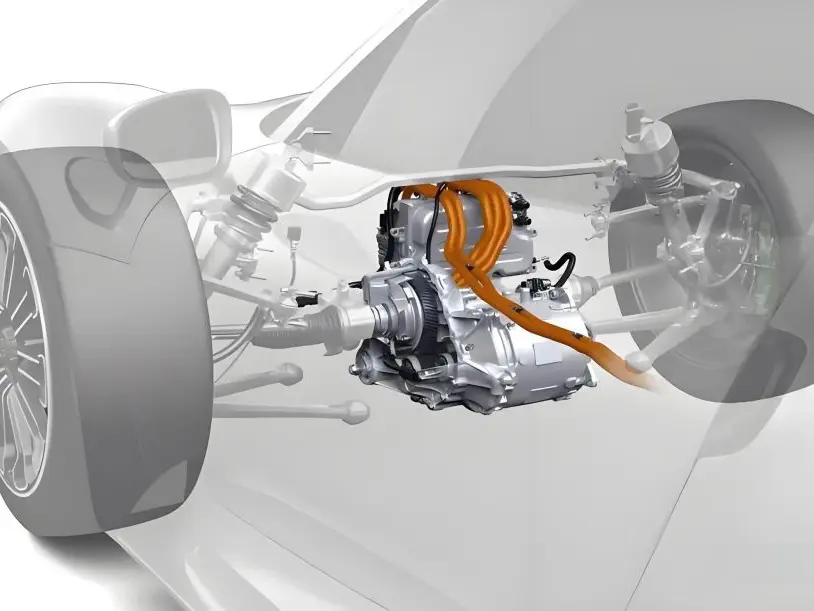
d) Installing the Electric Drive System
The electric drive system is the network of components that connects the motor to the wheels, allowing the car to move. This includes the controller, wiring, and potentially a custom-built drive system if the vehicle originally used a more complex multi-gear transmission.
- Controller: The motor controller regulates the flow of electricity from the battery pack to the motor. It acts as the brain of the system, determining how much power the motor receives based on throttle input from the driver.
- Wiring and Power Distribution: A significant amount of rewiring is required to connect the new electric motor, battery, and controller to the car’s existing electrical system. This wiring must be insulated and routed carefully to avoid short circuits or damage from heat.
e) Charging System Integration
In an EV conversion, integrating a charging system is crucial. This allows you to recharge the car’s battery pack using standard electrical outlets or specialized charging stations.
- Onboard Charger: Most conversions include an onboard charger that is connected to the battery system. It allows you to charge the vehicle at home or at public charging stations.
- Charging Port: A charging port is installed on the car’s exterior to allow easy connection to the power source.
- Level 1 and Level 2 Charging: The charging speed can vary depending on the power supply. Level 1 charging (standard 110V outlets) is slower, while Level 2 (240V outlets) provides faster recharging times.
f) Testing and Calibration
After all components are installed, the vehicle undergoes rigorous testing to ensure that the new electric systems function as intended. This includes testing the motor for proper acceleration, ensuring the battery is correctly charged and discharged, and verifying that the car’s safety features, like brakes and suspension, are functioning correctly. Calibration may also include adjusting the throttle response, fine-tuning the motor controller, and making adjustments to ensure optimal performance.

Benefits of EV Conversion
Converting your gas-powered vehicle to electric brings with it several significant advantages. Whether you're motivated by environmental concerns, financial benefits, or performance enhancements, EV conversion offers a compelling solution for many car owners.
a) Environmental Impact
The most obvious benefit of EV conversion is the positive environmental impact. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which can help reduce pollution in urban areas. In regions where electricity is generated from renewable sources, the carbon footprint of driving an EV can be close to zero.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Unlike gasoline-powered cars, which release harmful emissions into the atmosphere, electric vehicles don’t contribute to air pollution or global warming.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are significantly more efficient than internal combustion engines. An EV typically converts more than 85% of the energy from the battery into movement, whereas a gas engine only manages about 20% efficiency.
b) Cost Savings on Fuel
One of the most attractive benefits of EV conversion is the potential for savings on fuel costs. The cost of electricity per mile is generally far lower than gasoline, meaning the cost of running an electric vehicle is often much cheaper than operating a traditional gas-powered car.
- Lower Operating Costs: The average cost to charge an EV is significantly lower than filling a gas tank. For example, the cost of charging a car at home is usually about half the price of gasoline, even with fluctuating electricity rates.
- Savings Over Time: The cost savings on fuel will add up over the life of the vehicle, making an EV conversion a financially beneficial long-term investment.
c) Reduced Maintenance
Electric vehicles are much simpler than gas-powered cars and have fewer moving parts, which results in fewer repairs and maintenance requirements.
- No Oil Changes: EVs don’t need oil changes, which are a recurring expense for traditional vehicles.
- Fewer Parts to Wear Out: With no exhaust system, fewer moving parts, and no need for a complex transmission system, electric vehicles are far less prone to mechanical failure, reducing maintenance costs over time.
d) Increased Vehicle Longevity
Electric motors are designed to last much longer than internal combustion engines. As EVs generally have fewer components that wear out, a converted vehicle may last significantly longer than it would with a gasoline engine.
- Longer Motor Life: An electric motor can easily last 100,000 to 200,000 miles or more with minimal degradation.
- Preservation of the Car's Value: By converting an older car to electric, you can extend its life and maintain its value, especially if the car has sentimental or historical value.
e) Performance Improvements
Electric vehicles provide a smooth, quiet, and powerful driving experience. The electric motor delivers instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration without the need to rev an engine.
- Instant Torque: Unlike gas-powered engines, which require time to build up power, electric motors provide immediate power as soon as you hit the accelerator.
- Silent Operation: One of the biggest changes you’ll notice after conversion is the quietness of the vehicle. EVs are much quieter than gasoline cars, making for a smoother, more enjoyable ride.
f) Government Incentives
In some countries, governments offer tax incentives and rebates to encourage individuals to convert their gasoline-powered cars to electric. These incentives can help offset the initial cost of conversion.
Cost of an EV Conversion
The cost of converting a gas-powered vehicle to electric can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the conversion, the type of car, and the components chosen. It is essential to be aware of both the initial costs and potential ongoing expenses.
a) Initial Conversion Costs
- DIY Conversion: A DIY conversion can be much cheaper, especially if you’re able to source a cheap EV conversion kit or repurpose parts from existing electric vehicles. DIY conversions typically range from $6,000 to $12,000, but this can increase depending on the complexity of the project and the type of car.
- Professional Conversion: If you hire professionals to do the conversion, you should expect to pay anywhere between $20,000 and $50,000 for the complete job, depending on the components used, the car's size, and the labor involved.
b) Electric Car Conversion Kit Prices
The cost of an EV conversion kit can range from $4,000 to $10,000. These kits typically include the electric motor, controller, and necessary wiring and components to convert a car. Some kits also include a battery pack, while others leave it up to the owner to purchase separately.
c) Battery Pack Cost
The battery pack is usually the most expensive component of the conversion, and it can account for up to 50% of the total cost. A decent lithium-ion battery pack can cost anywhere from $3,000 to $10,000 depending on its size and energy capacity.
d) Ongoing Costs
Once the conversion is completed, the ongoing costs are relatively low. Charging the vehicle will cost significantly less than refueling with gasoline, and the maintenance costs are generally much lower than for a gasoline-powered car.
Which Cars Can Be Converted?
Almost any car can be converted to electric, but some are better suited for conversion than others. Generally, lighter cars are easier to convert, and vehicles with simpler mechanical systems require less work.
a) Best Candidates for EV Conversion
- Older Vehicles: Classic cars and vintage models are often the best candidates for EV conversion. They typically have less complex electronics and mechanical systems, making them easier to retrofit.
- Small and Light Cars: Smaller cars tend to be better suited for EV conversions because they require less power to move. Sports cars, small hatchbacks, and even compact sedans are popular choices.
b) Cars That Are Harder to Convert
- Newer Vehicles: Modern vehicles with complex electronics, advanced safety features, and proprietary systems can be challenging and costly to convert.
- Heavy Trucks or SUVs: Larger vehicles often require larger battery packs and more powerful motors, making conversions more expensive and complicated.
Gas to Electric Car Conversion Kit: A Brief Look
EV conversion kits are available for many types of vehicles, offering various components to help make the process easier. These kits range from budget-friendly options to high-performance setups. When considering an EV conversion, many DIY enthusiasts turn to gas to electric car conversion kits as a starting point. These kits include the essential components needed for the conversion and often come with detailed instructions to help you complete the job. Depending on the kit, additional components like batteries, motors, and controllers may need to be purchased separately.
a) Cheap EV Conversion Kits
For those on a tight budget, there are cheap EV conversion kits available that provide basic components, such as the motor and controller, but may not include a battery or other advanced features. These kits are ideal for DIY enthusiasts looking for an affordable way to convert their car without breaking the bank.
b) Complete EV Conversion Kits
For those looking for a more comprehensive solution, many providers offer gas to electric car conversion kits that include everything from the motor and battery pack to the charging system and wiring. These kits are more expensive but can save time and effort when compared to piecing together your own conversion components. A gas to electric car conversion kit typically costs between $2,000 and $5,000, and includes many of the essential parts for the conversion, such as the motor, controller, and wiring systems.
c) Custom Solutions
For unique projects or high-performance conversions, you can find companies that will create custom kits tailored to your specific vehicle and needs. Custom kits allow for more flexibility but can also add to the overall cost.

Conclusion
Converting a gas-powered vehicle to electric is an exciting and sustainable option that offers numerous benefits, from cost savings to improved performance. While the conversion process requires substantial investment and technical expertise, it is a rewarding project for those looking to reduce their environmental impact and experience the perks of electric driving.
With a variety of cheap EV conversion kits available, the dream of owning an electric car is now more achievable than ever. Whether you are embarking on a DIY project or opting for a professional conversion, this guide has hopefully provided the insight needed to make your transition from gas to electric as smooth and enjoyable as possible.
By selecting the right gas to electric car conversion kit, you can unlock the full potential of your vehicle, making it a cleaner, more efficient, and ultimately more rewarding ride.