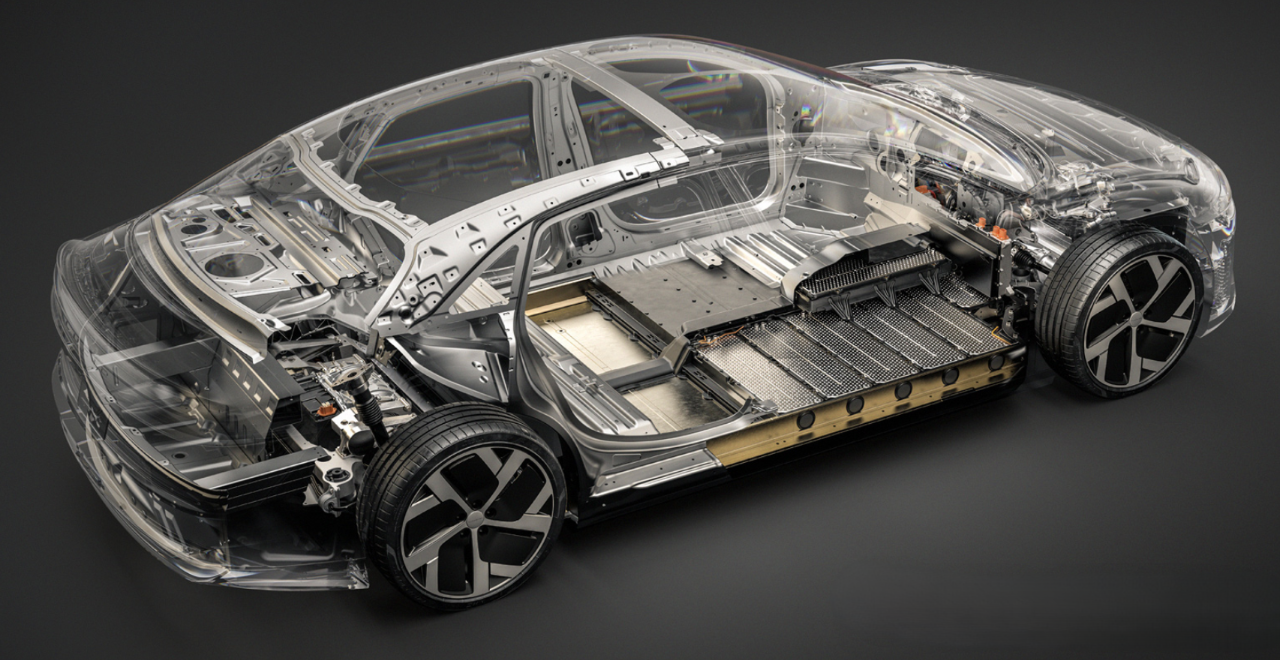
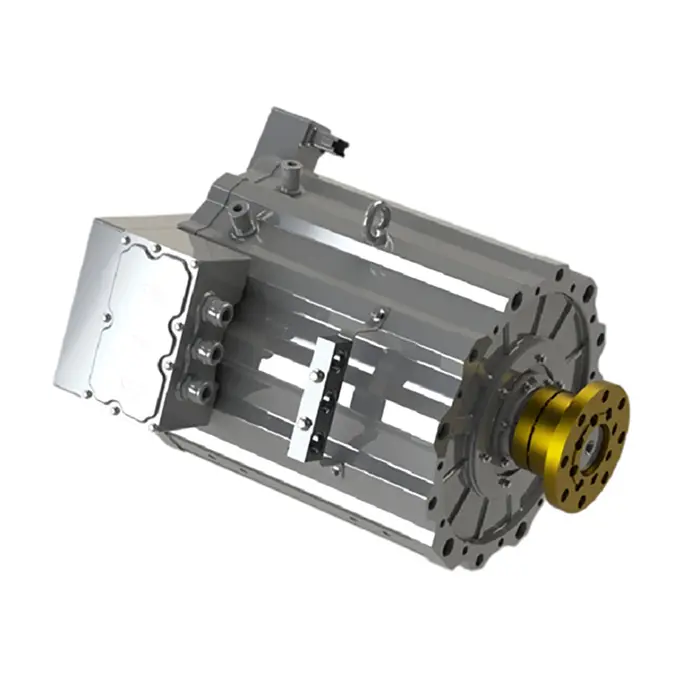
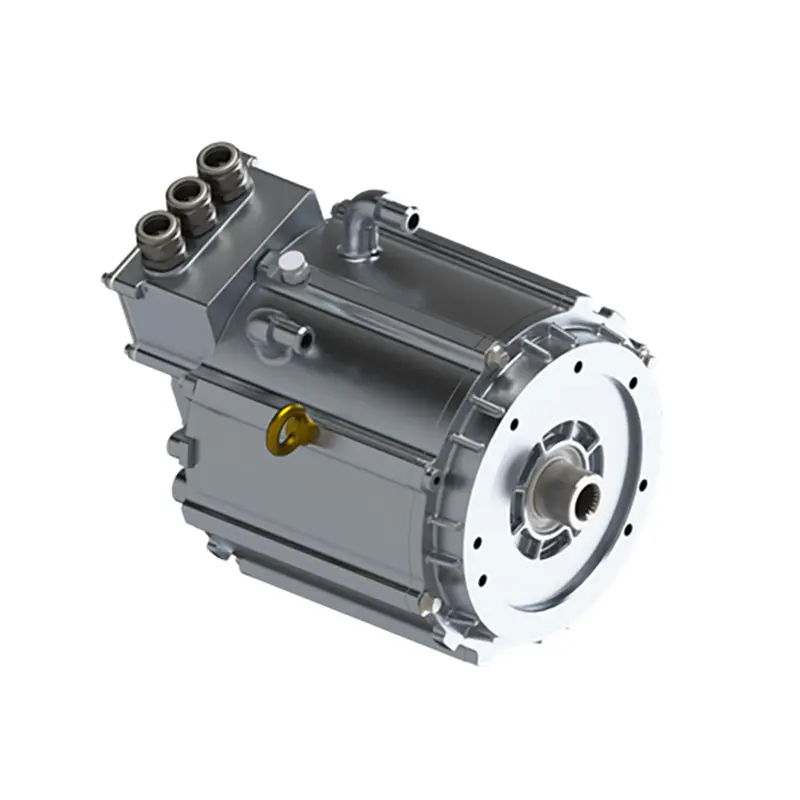
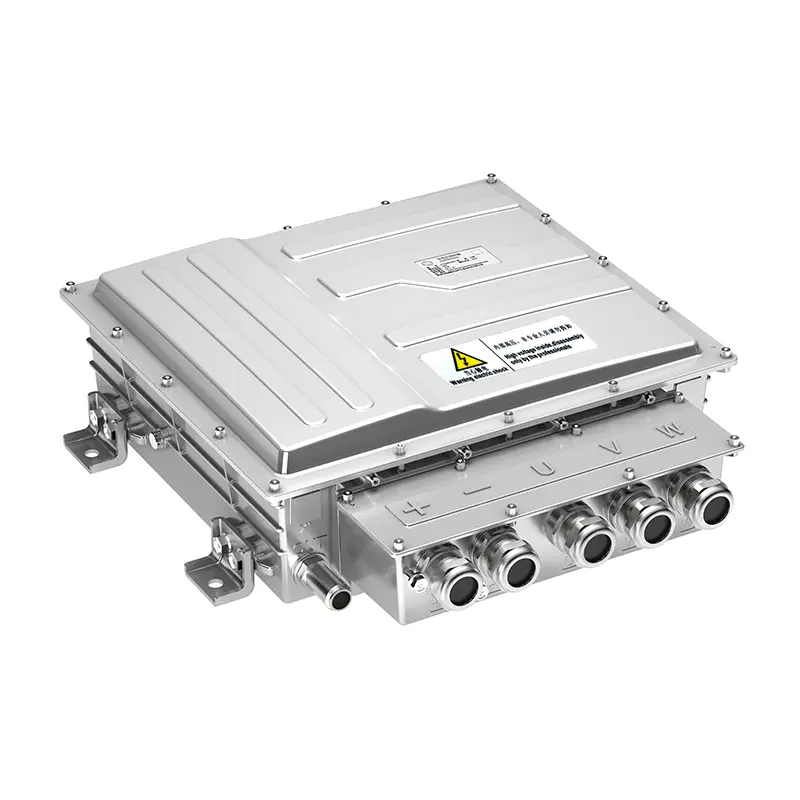
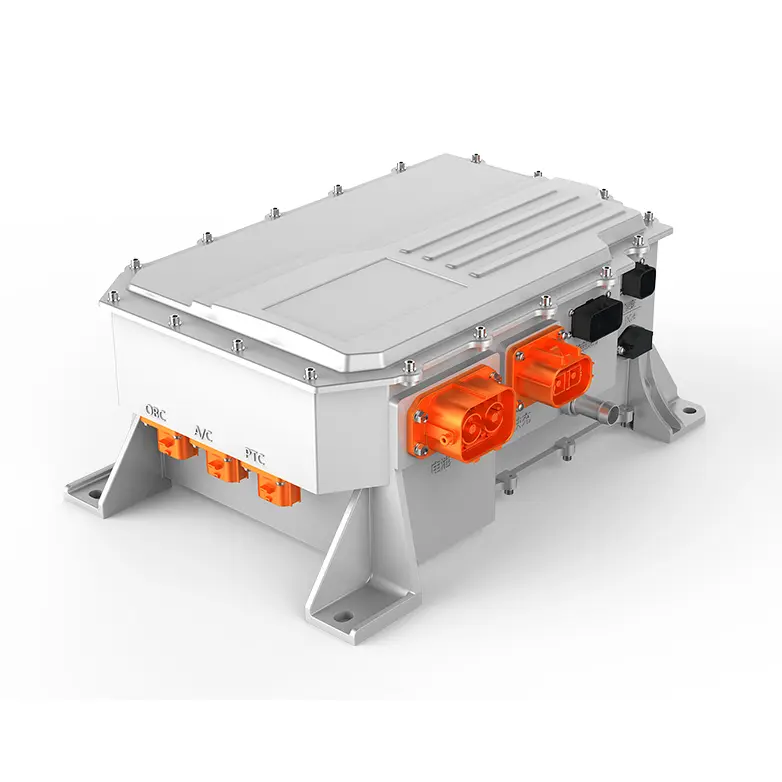
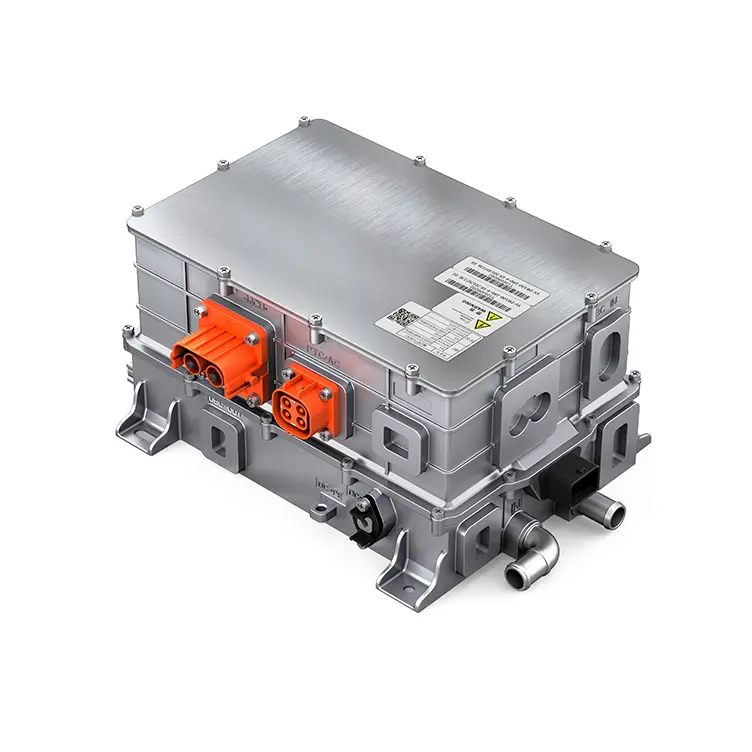
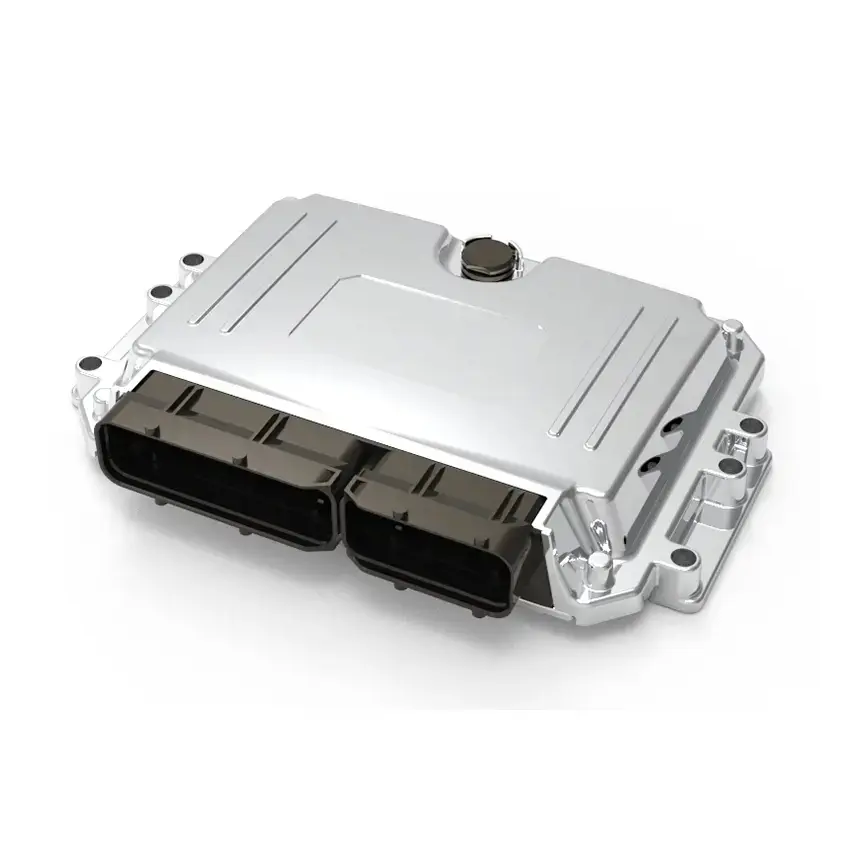
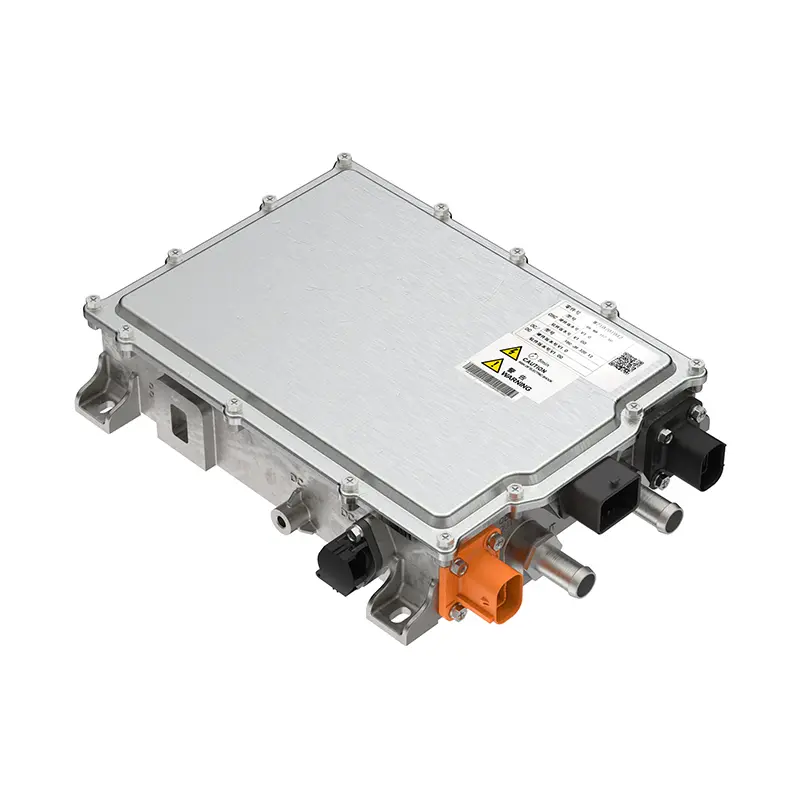
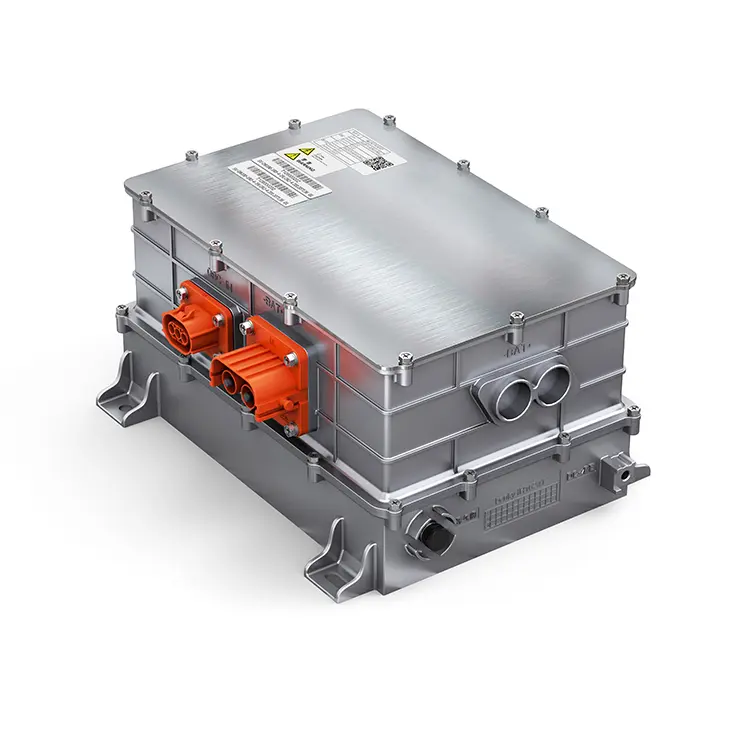
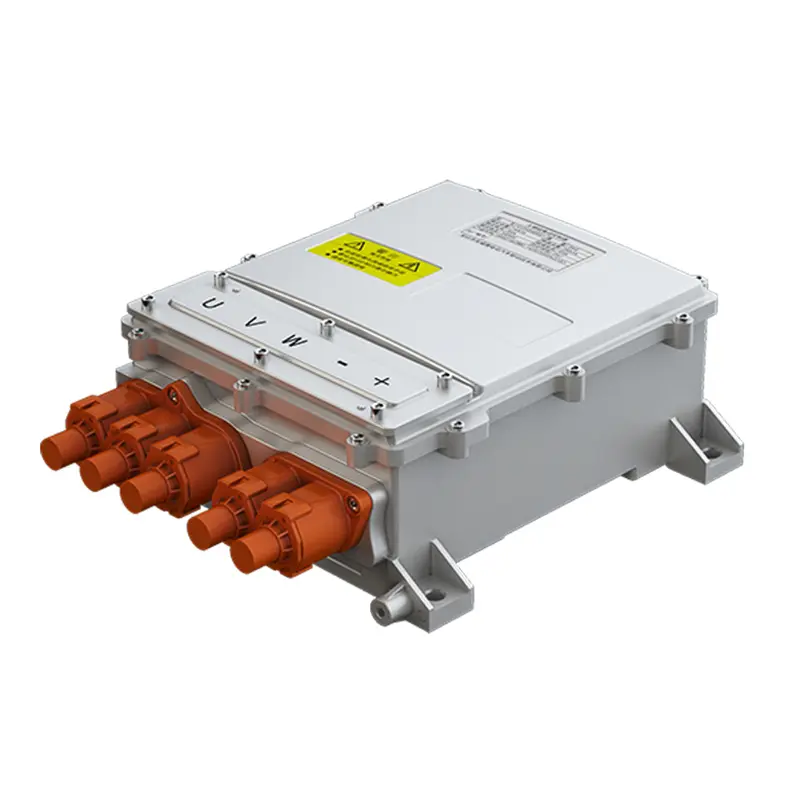
PUMBAA power conversion & distribution for electric vehicles PPS570
Main Components of Vehicle power conversion & distribution Conversion & Distribution Unit(CDU)
(1) OBC, or On-Board Charger, mainly converts single-phase AC or three-phase AC into DC to charge the vehicle power battery.
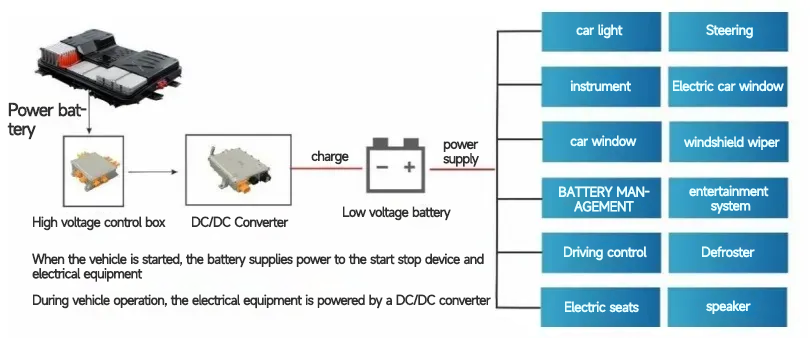
(2) DC/DC converter for electric vehicles mainly converts the high-voltage DC power output from the power battery into low-voltage DC power to supply power to the low-voltage power equipment of the vehicle.
(3) PDU is the high-voltage power distribution unit, which is a centralized power distribution scheme for new energy vehicles, with compact structure design, convenient wiring layout and convenient maintenance.
description2
Benefits of Electric Vehicle power conversion & distribution Conversion & Distribution Unit(CDU)
(1) 15% reduction in product weight, 20% reduction in volume, and 5% reduction in low-speed power consumption costs;
(2) Expandable modular platform, which can be extended to match different models, greatly shortening the product development cycle and saving costs;
(3) Frequency conversion and multi-vector decoupling control algorithm, effectively improving motor dynamic response and NVH characteristics;
(4) Perfect fault diagnosis and safety monitoring mechanism, effectively ensure the vehicle high voltage safety, torque safety and high temperature safety.
Conform with EU standard
Support vehicle-to-vehicle charging (V2V)
Support vehicle-to-load charging (V2L)
All-automotive-grade device design
Bidirectional power conversion
Support UDS diagnosis
Support OTA upgrade and rollback
Applicable to BEV, PHEV, REEV,2.5/3.5T
Minivans, Minitrucks, passenger cars, commercial vehicles, buses, professional vehicles and other types of new energy vehicles
description2
Application

Passenger car, Minivans, Mini trucks

2.5T Electric Minivan

3.5T Electric Minivan
description2
Specification of Electric Commercial Vehicle power supply
|
DCDC |
Input characteristics |
High Voltage |
200-450V |
|
Low pressure |
12V |
||
|
Output characteristics |
Power |
Rating:1.5kW Peak:1.8kW |
|
|
Output voltage |
14VDC |
||
|
Output Current |
Rating:108A Peak:128A |
||
|
OBC |
Input characteristics |
High Voltage |
85~264VAC |
|
Low pressure |
12V |
||
|
Output characteristics |
Power |
3.3KW |
|
|
Output voltage |
200~450VDC |
||
|
Maximum output current |
10A |
||
|
PDU |
Function 1 |
Batteries (standard) |
|
|
Function 2 |
Main Drive (standard) |
||
|
Function 3 |
Electric air conditioner (standard) |
||
|
Function 4 |
PTC (standard) |
||
|
System characteristics |
Operating temperature |
-40~80℃ |
|
|
Cooling mode |
Water cooling |
||
|
Size |
189W×281D×121H(mm) |
||
|
Weight |
About 10 kg |
||
|
Protection level |
IP67 |
||
description2
Power Conversion& Distribution System (OBC, DCDC, PDU)
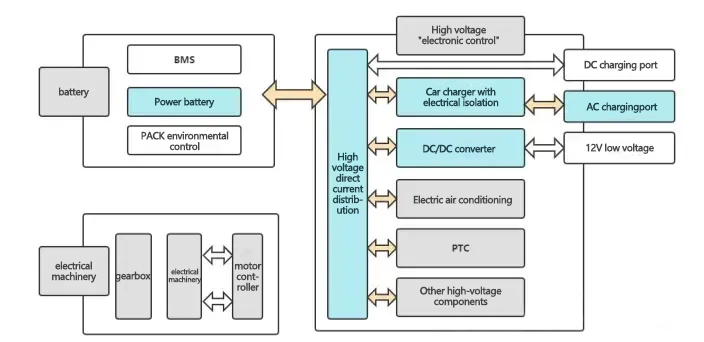
Power conversion and distribution system refers to the vehicle charger (OBC), EV DC/DC converter, high-voltage power distribution box (PDU), as the core parts of the electronic control, plays an important role in the conversion and transmission of AC and DC energy. Power conversion and distribution system development trend: integration, multifunctionality, high power into.
The on-board charger (OBC) is an important electronic device that connects to the AC charging post and converts AC power to DC power (AC DC power conversion) ; the on-board DC/DC converter converts the high-voltage power output from the power battery into the low-voltage required by each electrical appliance; the PDU is a high-voltage power distribution unit that distributes the DC power output from the battery and monitors the over-current and over-voltage.
Electric vehicle components mainly include powertrain system (power battery, electric motor controller, ev motor) and power conversion and distribution systems (on-board charger EV OBC, EV DC/DC converter, high voltage distribution box PDU).
1. OBC
Electric vehicle charging can be divided into two kinds of AC charging and DC charging, 1) DC charging “fast charging”, the use of external “DC charging pile” directly to the power battery charging, without the use of on-board charging machine; 2) AC charging “Slow charging”, AC charging piles supply single-phase AC (220V) or three-phase AC (380V) current from the AC grid to the on-board charger (OBC) installed in the vehicle, and the OBC can convert AC power into DC power to charge the new energy vehicle.
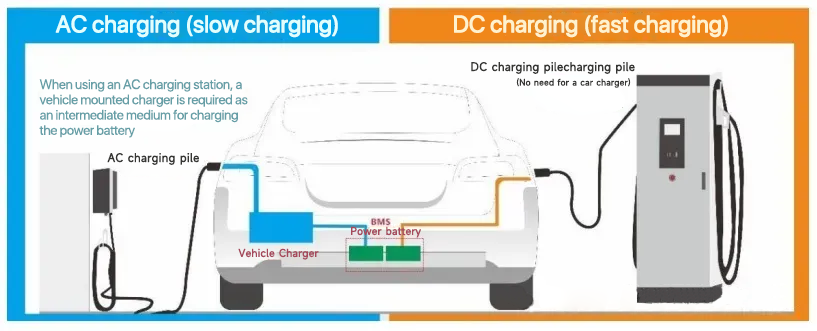
New Energy Vehicle Charging Method Schematic
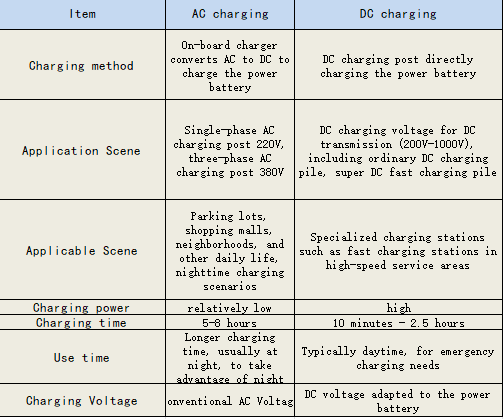
Comparison of AC and DC charging
On-board chargers (OBC) can realize the slow charging function of electric vehicles. OBC are mounted on electric vehicles and connected to AC charging piles during charging to convert AC power into DC power (AC-DC powder conversion) for slow charging of power batteries. 400V OBC are mostly 3.3 or 6.6kW, while 11.22kW OBC have been developed to meet the charging demand of 800V and may become the mainstream power in the future.
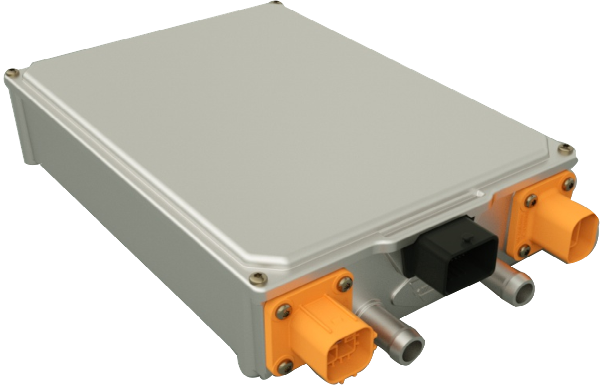
Schematic diagram of the appearance of on-board charger (OBC)
2. DC/DC
EV DC/DC converter (DC-DC converter) draws power from the power battery and charges the 12V or 24V low-voltage battery in the vehicle. DC/DC can convert a certain value of DC power supply voltage output from the power battery to another value of DC power supply voltage, and play the role of regulating power supply output and stabilizing power supply voltage. Usually, it can be divided into three kinds: high-voltage to high-voltage DC/DC converter, high-voltage to low-voltage DC/DC converter, and low-voltage regulator DC/DC converter.
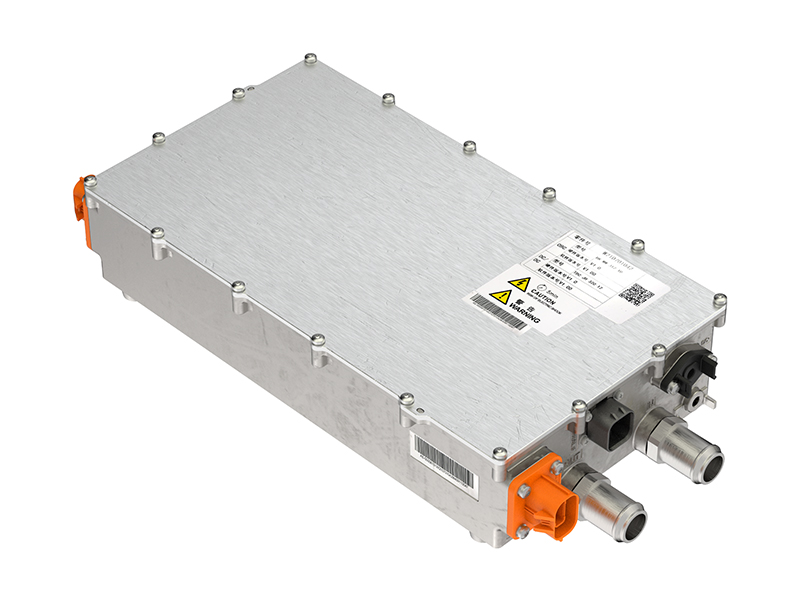
DC/DC converter external schematic
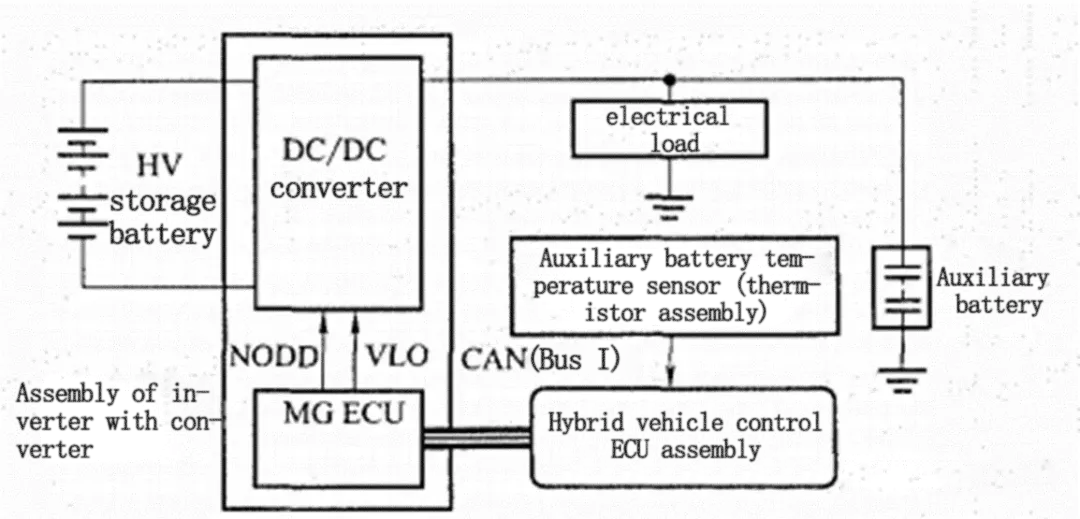
Schematic diagram of the operating principle of the automotive DC/DC converter
The input of the on-board DC/DC converter for is connected to the high-voltage output of the power battery, and the output is connected to the low-voltage appliances and the battery in parallel. When the VCU (vehicle controller) does not receive the high-voltage command, the battery supplies power to the low-voltage appliances. When VCU receives high voltage command, EV DC/DC converter will start, and the high voltage power output from power battery will be converted by DC/DC converter for electric vehicles to output stable low voltage power. EV DC/DC converter should supply power to low voltage appliances and battery according to the actual power consumption of vehicle electrical appliances and the charging/discharging balance of battery.
3. PDU
High-voltage Distribution Unit (PDU) is a high-voltage power distribution unit that distributes the DC power output from the battery and monitors the over-current and over-voltage in the high-voltage system. PDU connects the power battery and controls the charging and discharging through the busbar and wiring harness, and distributes the DC power output from the power battery to the high-voltage electrical appliances of the automobile, such as OBC, on-board DC/DC converter for electric vehicles, motor controller, air conditioner, PTC and so on, and it plays a function of overload and short-circuit protection, low voltage control, etc., to protect and monitor the operation of the high-voltage system. In the high-voltage system, it plays the role of overload and short-circuit protection, low-voltage control and other functions to protect and monitor the operation of the high-voltage system.
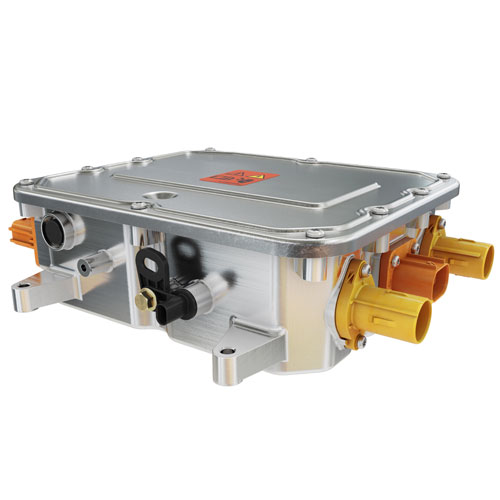

Appearance diagram of high voltage power distribution box (PDU)
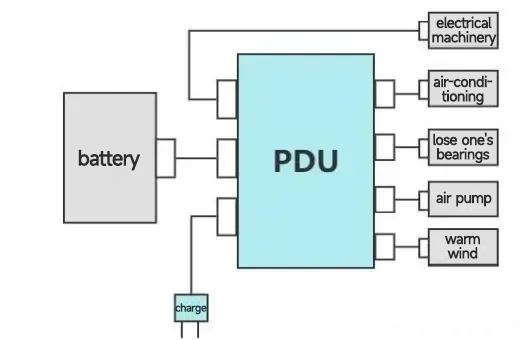
PDU Function Diagram
Trend 1: High-power
Solution to charging anxiety, many car companies choose high-voltage fast charging. To solve charging anxiety, there are two modes: high-voltage fast charging and power exchange; Azalea and Geely Ruilan layout power exchange mode; Porsche Tycan is the first 800V fast-charging model; after Porsche, BYD, Dongfeng Lantu, Geely, Xiaopeng and other automobile enterprises lay out high-voltage fast-charging, and Xiaopeng G9 has become the first 800V high-voltage SiC car model.
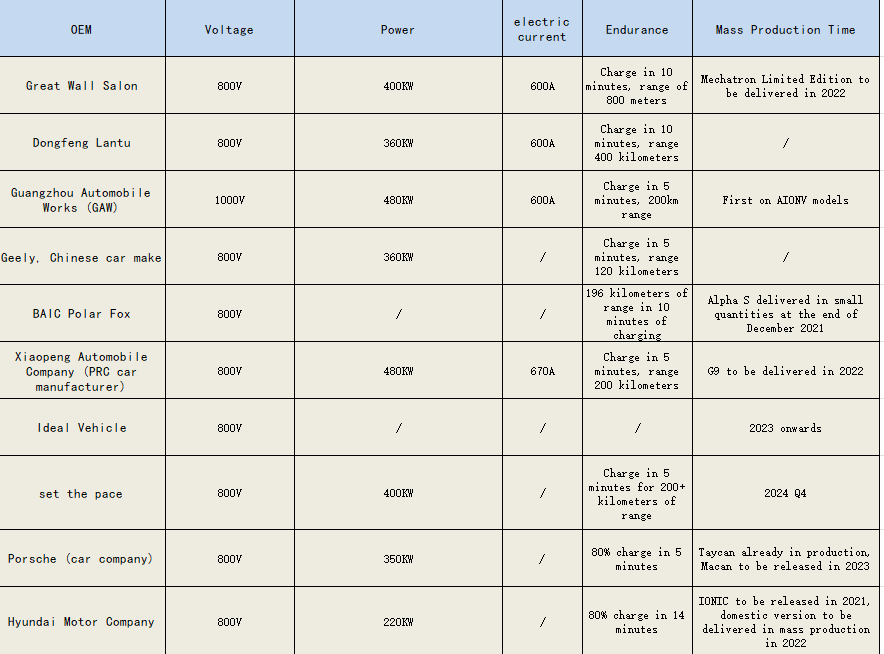
High-voltage fast charging becomes the main trend
Trend 2: Integration
The mainstream trend is the integrated design of OBC, DC/DC, PDU and other components. Integration of power conversion and distribution system can realize 1) lightweight, reduce the total weight of power supply device, promote electric vehicle lightweight, improve range and reduce costs is an important development direction for electric vehicle enterprises, 2) reduce costs, after integration, the value of a single vehicle decreases, reduce the number of parts that need to be assembled in the production process of the whole vehicle, so as to reduce the cost of the vehicle enterprise, the cost of the integration decreased by $700-800.
Trend 3: Multi-functional
Unidirectional on-board DC/DC converters for electric vehicles are evolving into bi-directional types, which can reduce costs by replacing the associated devices for pre-charging bus capacitors and reducing the use of zero components. The bi-directional DC/DC can realize the bi-directional flow of power, converting low voltage power to high voltage power. When the motor accelerates, the battery is discharged through DC/DC ev charger; when the motor brakes, the braking energy charges the battery through DC/DC, which reduces energy loss and improves vehicle range. Bidirectionalized OBC plays the role of mobile distributed energy storage. Traditional unidirectional vehicle chargers can only meet the one-way flow of energy, which flows from the power grid to the power battery through the OBC. Bidirectionalization means that through the inverter technology of OBC, energy can flow from the power battery to other electrical appliances via OBC, thus enabling new energy vehicles to meet the function of emergency charging in daily life.
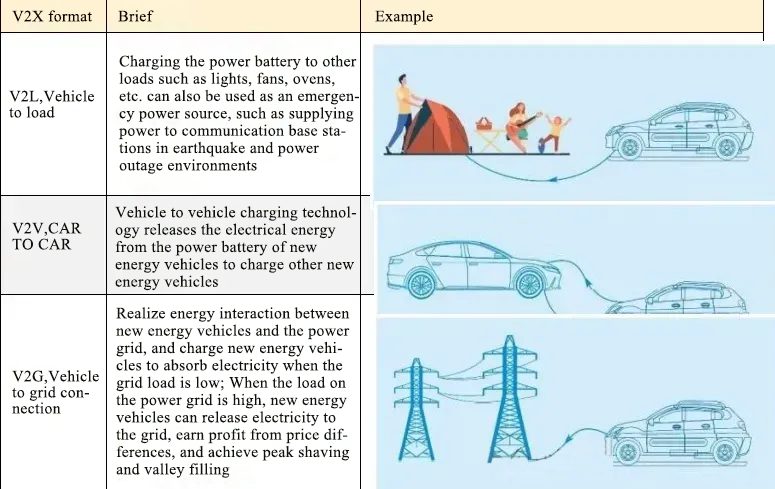
Bidirectional OBC Application Scenarios
description2
Blog

China’s getting a big electric car battery swapping boost in 2025. Would that work across the globe?

Pumbaa's Superior Electric Motor Service: Leading sales center for electric motors
EVs Could Last Much Longer Than You Think