10 Main Component Of Electric Vehicle: The Ultimate Guide
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the automotive industry by offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional gasoline-powered cars. As the demand for EVs grows, understanding their core components becomes essential for consumers, engineers, and enthusiasts alike. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs rely on electricity to power their systems, eliminating fuel dependency and significantly reducing carbon emissions.
This guide explores the 10 main component of electric vehicles, highlighting their functions, types, and significance. Whether you're considering an EV purchase or simply curious about their technology, this article will provide a detailed breakdown of the parts of electric vehicle and how they contribute to overall performance.
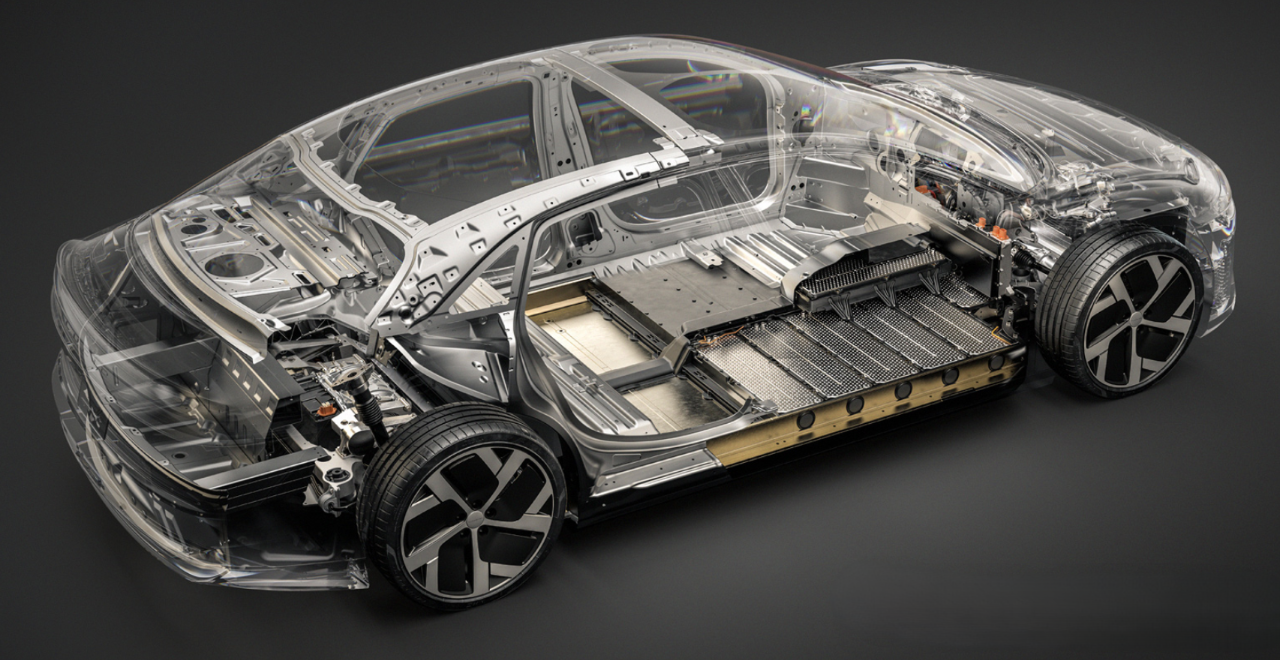
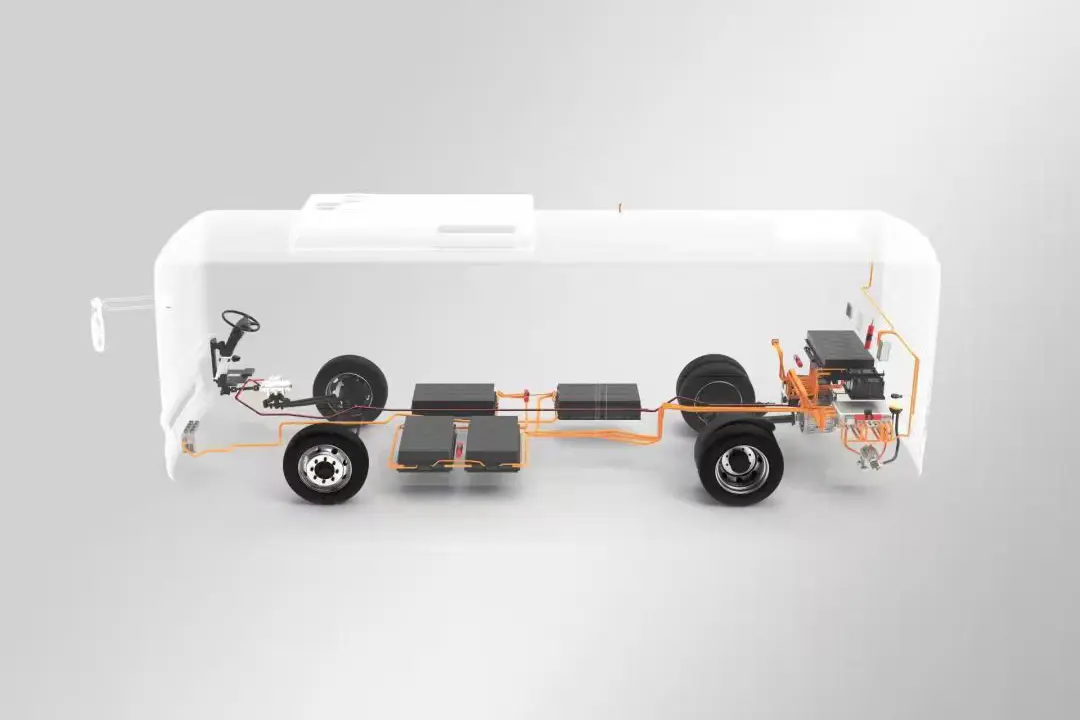
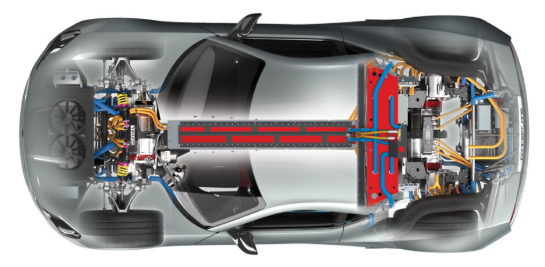
Battery Pack
The battery pack is the most crucial component of an electric vehicle, serving as the primary source of energy. It determines the vehicle's range, efficiency, and charging speed.
Functions:
- Stores and supplies electrical energy to the motor and other components.
- Determines the vehicle’s driving range based on its capacity.
- Impacts the overall cost and weight of the EV.
Types of Batteries:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries (Li-Ion): Most commonly used due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and quick charging capabilities.
- Solid-State Batteries: A promising future technology offering higher safety and energy storage.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: Found in hybrid vehicles but less efficient than Li-Ion.
A high-quality battery pack is essential for efficient energy storage and long-term performance, making it one of the most expensive parts of electric vehicle.
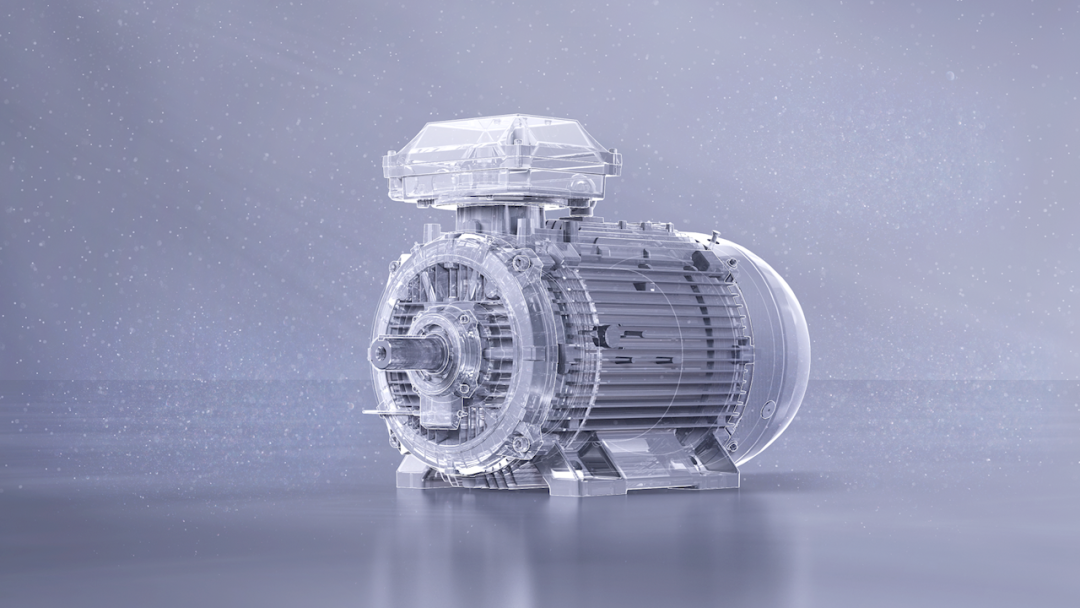
Electric Motor
The electric motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors provide instant torque, leading to quicker acceleration and smoother driving.
Functions:
- Converts electrical energy into rotational force (torque).
- Determines acceleration and top speed of the EV.
- Operates with minimal energy loss and high efficiency.
Types of Electric Motors:
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM): Highly efficient, widely used in modern EVs.
- Induction Motor (IM): Durable and reliable, used in early Tesla models.
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM): Offers cost advantages but has lower efficiency.
Instant torque delivery from electric motors ensures smooth and responsive driving performance, making them one of the key main component of electric vehicles.
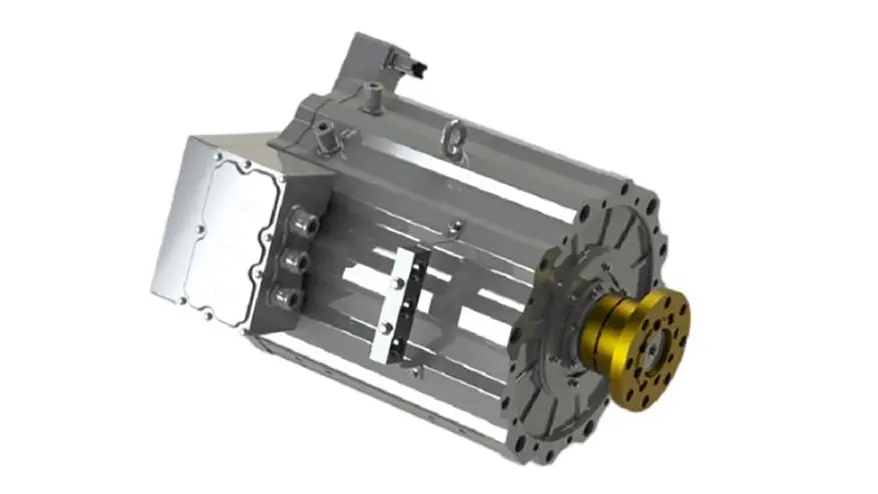

Inverter
The inverter is an essential electronic component that transforms direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) to power the electric motor.
Functions:
- Converts DC electricity from the battery into AC for the motor.
- Regulates motor speed and torque.
- Enhances energy efficiency and driving performance.
- Since most EV motors operate on AC, the inverter is indispensable in ensuring proper energy conversion and utilization.
Importance of the Inverter:
Since most EV motors operate on AC, the inverter is indispensable in ensuring proper energy conversion and utilization. The inverter also plays a crucial role in regenerative braking, allowing the vehicle to recover and store energy when decelerating. Advanced inverters include silicon carbide (SiC) technology, which improves efficiency, reduces heat generation, and extends battery life. Additionally, modern inverters come with smart control systems, enabling real-time adjustments to power output based on driving conditions.
Inverter performance directly affects vehicle efficiency, acceleration, and overall driving experience. High-performance inverters help reduce energy losses, contributing to extended range and improved battery longevity. As EV technology advances, bi-directional inverters are emerging, allowing energy to flow back to the grid (vehicle-to-grid technology), enhancing energy management in smart grids and home power systems.

Power Electronics Controller
The power electronics controller functions as the brain of the EV, managing power distribution between the battery, motor, and other electrical components.
Functions:
- Controls the amount of power delivered to the motor.
- Enhances energy efficiency and performance.
- Regulates torque and acceleration settings for smooth operation.
By optimizing energy use, the power electronics controller helps maintain efficiency while ensuring optimal driving performance.
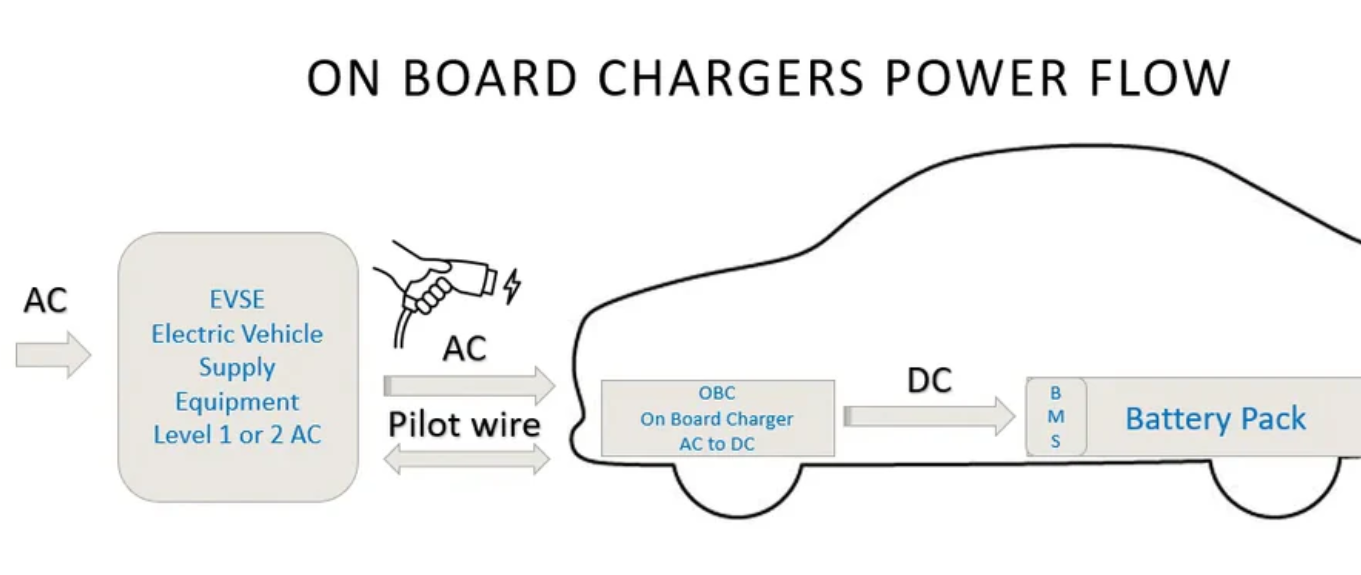
Charging System
The charging system enables the battery pack to recharge using an external power source. Charging infrastructure varies in terms of speed and efficiency, affecting how long it takes to replenish battery levels.
Functions:
- Converts AC power from the grid into DC power for battery storage.
- Manages charging speed and efficiency.
- Supports different charging levels based on power availability.
Charging Levels:
- Level 1 (120V AC): Standard home charging, slow (8-12 hours for a full charge).
- Level 2 (240V AC): Faster home and public charging (4-6 hours).
- DC Fast Charging: High-speed charging stations capable of providing 80% charge in 30-45 minutes.
The efficiency of an EV’s charging system directly affects user convenience and vehicle usability.
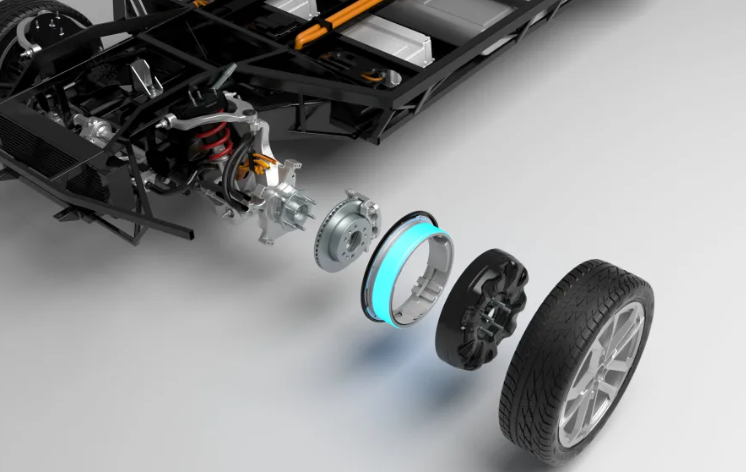
Transmission System
The transmission system in an electric vehicle differs significantly from that of traditional gasoline-powered cars. Most EVs use a single-speed transmission, simplifying power delivery.
Functions:
- Transfers power from the motor to the wheels.
- Ensures smooth acceleration and efficiency.
- Reduces mechanical complexity and maintenance costs.
EV transmissions are simpler and more efficient than traditional gear-based systems, enhancing reliability and longevity.
Thermal Management System
The thermal management system is crucial for maintaining optimal temperature conditions for the battery, motor, and power electronics. Since EV components generate heat, efficient cooling is necessary for performance and safety.
Functions:
- Prevents overheating of critical components.
- Improves efficiency and lifespan of the battery and motor.
- Regulates cabin temperature for passenger comfort.
Cooling Methods:
- Liquid Cooling: Efficient and widely used in high-performance EVs.
- Air Cooling: Less effective but used in budget-friendly models.
- Phase Change Materials (PCM): A developing technology for improved heat regulation.
Efficient thermal management is crucial for maintaining battery performance and ensuring safe operation.
DC-DC Converter
The DC-DC converter is responsible for converting high-voltage DC power from the battery to a lower voltage suitable for auxiliary systems, such as lights, infotainment, and climate control.
Functions:
- Converts high-voltage DC power from the battery to lower-voltage DC for auxiliary systems.
- Powers headlights, infotainment, and climate control systems.
- Ensures stable power distribution across the vehicle.
Without a DC-DC converter, EVs would require a separate battery for lower-voltage components, adding weight and complexity.
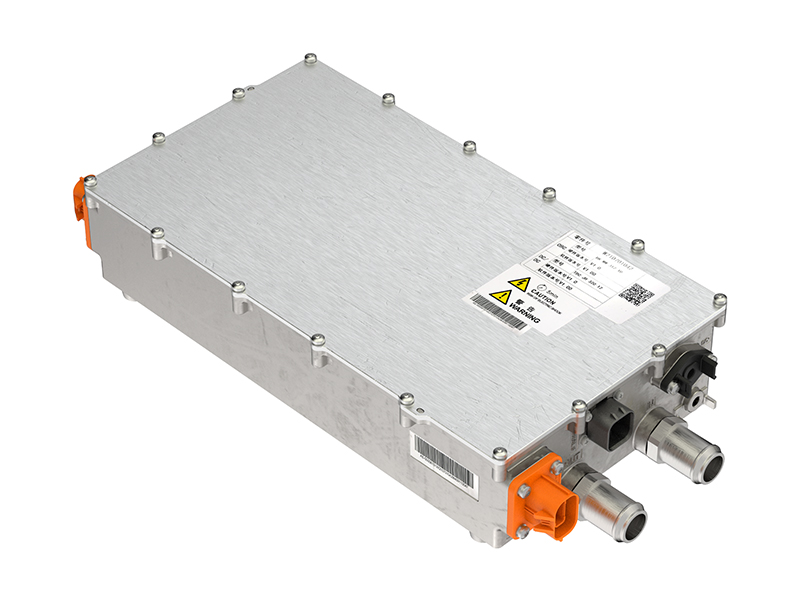
Regenerative Braking System
The regenerative braking system is a key innovation in EVs that recovers energy during braking and stores it back in the battery. This helps extend range and improve overall efficiency.
Functions:
- Converts kinetic energy into electricity and stores it in the battery.
- Improves vehicle efficiency and extends driving range.
- Reduces wear on mechanical braking components, lowering maintenance costs.
- Regenerative braking enhances energy conservation, making EVs more efficient than ICE vehicles.
Conclusion
Understanding the main component of electric vehicles is essential for appreciating their efficiency, reliability, and performance advantages over traditional cars. Each component, from the battery pack to the regenerative braking system, plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and energy-efficient driving experience.
As EV technology continues to evolve, advancements in battery technology, power electronics, and charging infrastructure will further enhance vehicle performance and sustainability. Whether you're a consumer looking to switch to an EV or an engineer interested in the mechanics of electric mobility, recognizing these key parts of electric vehicle provides valuable insights into the future of transportation.
With rapid innovations and an increasing shift towards clean energy, EVs represent the future of the automotive industry, driving us toward a more sustainable and eco-friendly world.
Read More: Top 6 Electric Conversion Kits Manufacturers for Your Car or Truck